Figure 1. Influenza A/WSN/33 (H1N1) virus infection reduces dark period activity and alters whole body metabolism in mice.
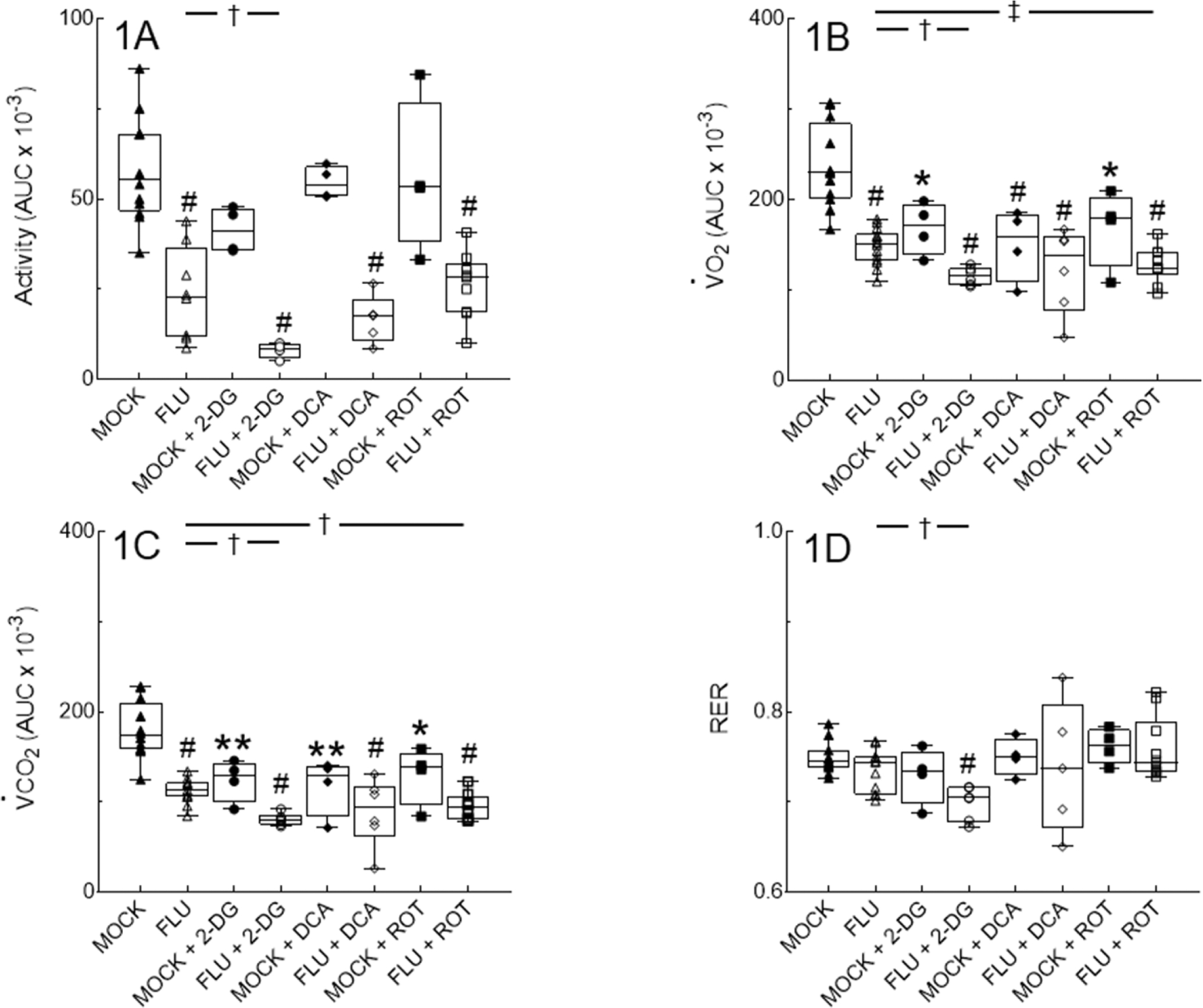
Effect of mock and IAV infection (FLU) and treatment with 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG; 0.76 g/kg, daily), dichloroacetate (DCA; 50 mg/kg, daily), or rotenone (ROT; 0.8 mg/kg. every other day) from 1–5 days post-inoculation (d.p.i.) on: (A) Nocturnal activity (expressed as area under curve [AUC]); (B) O2 consumption (V̇O2; expressed as AUC); (C) CO2 production (V̇CO2; expressed as AUC); and (D) Respiratory exchange ratio (RER). All measurements were made from 5–6 d.p.i. n=12, 8, 4, 4, 4, 5, 4, and 9 per group (from 12 individual mock or IAV infections). Data in box represent first quartile, median, and third quartile for each experimental group. Whiskers indicate highest and lowest sample values within the group. *: P<0.05, **: P<0.005, #: P<0.001, vs. mock-infected mice. †: P<0.05, ‡: P<0.005, vs. IAV-infected mice.
