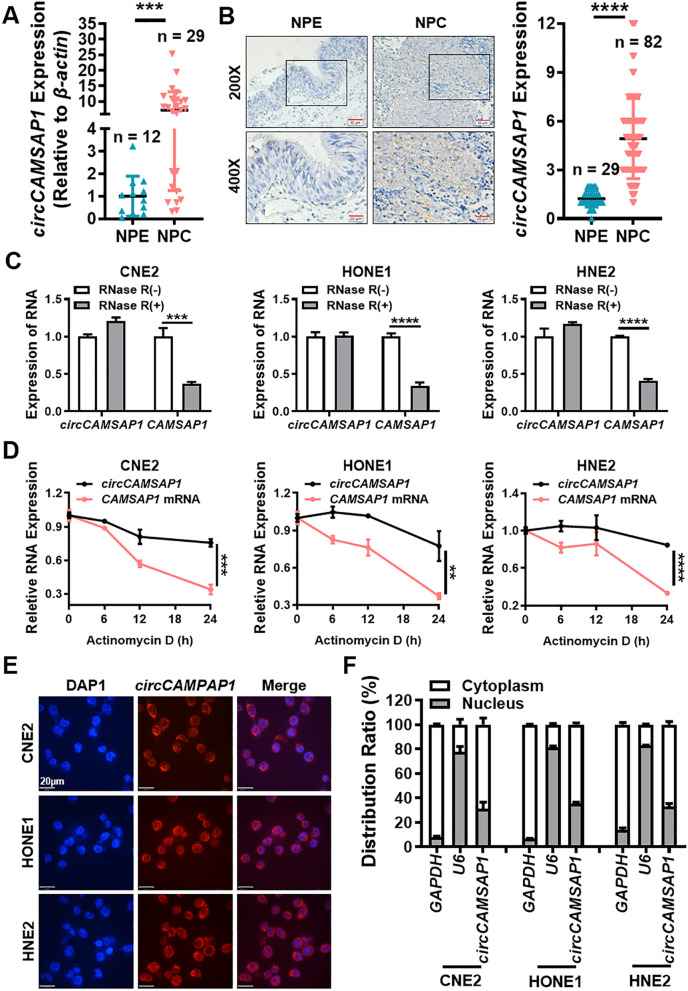
Fig. 1.
circCAMSAP1 is highly expressed in NPC. A The expression of circCAMSAP1 was measured in 29 NPC tissues and 12 non-cancerous NPE tissue samples by RT-qPCR. β-actin was used as an internal reference. NPE, nasopharyngeal epithelium; NPC, nasopharyngeal carcinoma. ***, p < 0.001. B Representative images of circCAMSAP1 in 82 NPC tissues and 29 adjacent NPE tissues by in situ hybridization. × 200, scale bar = 50 μm; × 400, scale bar = 20 μm. The statistical data was shown in the right panel. ****, p < 0.0001. C The stability of circCAMSAP1 was detected in three RNase R-treated NPC cells by RT-qPCR. CAMSAP1 mRNA was used as a negative control. ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001. D The stability of circCAMSAP1 was examined in NPC cells after treating with actinomycin D for 0, 6, 12 and 24 h. The relative RNA levels of circCAMSAP1 and CAMSAP1 mRNA in NPC cells were measured by RT-qPCR. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001. E Intracellular localization of circCAMSAP1 (red) in three NPC cells, as determined by fluorescence in situ hybridization using a digoxigenin-labeled circCAMSAP1 probe. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 20 μm. F The cellular localization of circCAMSAP1 was examined in three NPC cells by nuclear and cytoplasmic separation test. GAPDH and U6 were used as positive controls for cytoplasm and nucleus, respectively