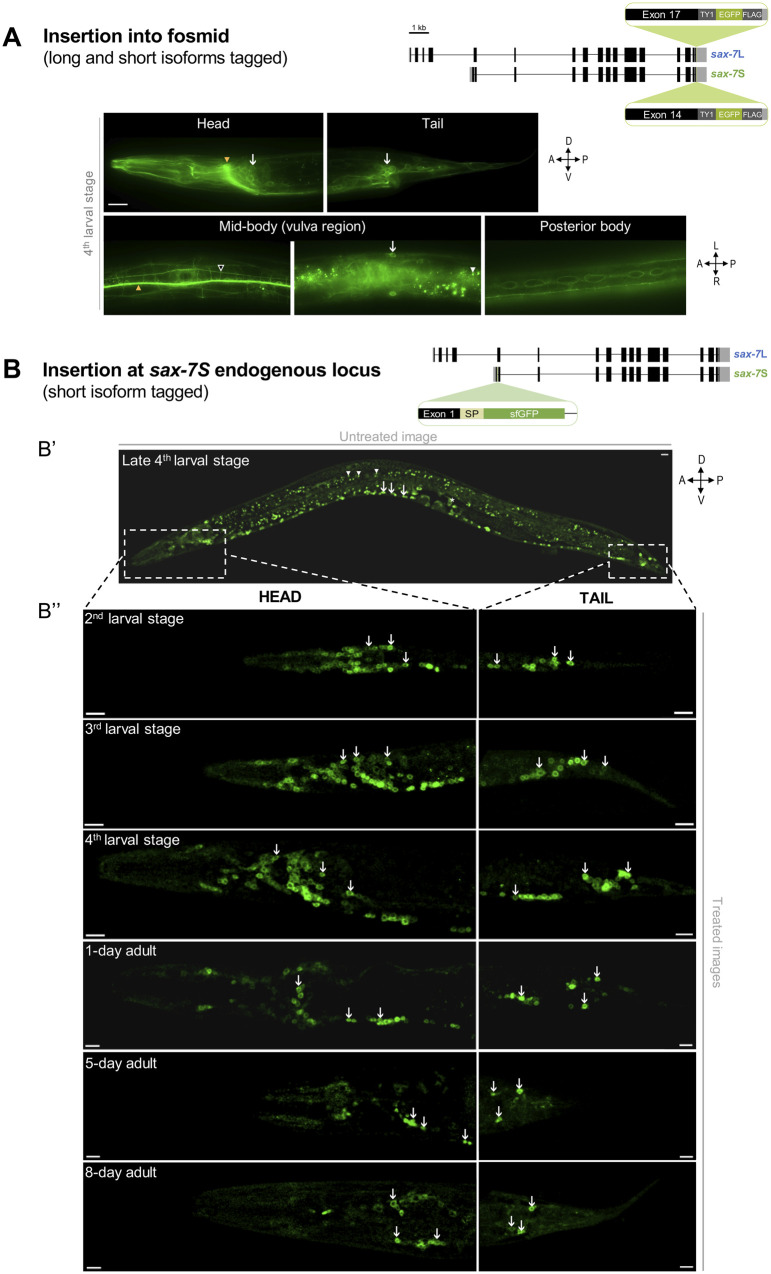
Figure 4.
SAX-7S is expressed in virtually all neurons throughout life. (A) Images of SAX-7::GFP expression reporting both SAX-7L and SAX-7S. As shown on the schematics, in this previously published transgene (Sarov et al. 2012), the gene coding for EGFP was inserted into the gene sax-7 by fosmid recombineering in such a way that both SAX-7S and SAX-7L isoforms were tagged, making it impossible to distinguish between them. SAX-7::GFP is broadly expressed in neurons and epidermal cells (vulval cells, seam cells). (B) Confocal images showing sfGFP::SAX-7S expression. As shown on the schematics, the gene coding for sfGFP was inserted by CRISPR-Cas9 at the end of exon 1 of sax-7S in order to specifically tag SAX-7S (see Supplementary Figure S1D; qv31 in Table 1). “sfGFP,” superfolderGFP; “SP,” export signal peptide sequence part of sax-7S inserted along with sfgfp. (Bʹ) Untreated confocal image of a late 4th larval stage worm. Arrows indicate neurons of ventral nerve cord and arrowheads point to examples of background green auto-fluorescence due to gut granules. Dotted boxes indicate the body region (head or tail) analyzed in B″. (B″) Images of animals at the indicated larval stages and days of adulthood examined by confocal microscopy followed by unmixing. Aged worms (>5-day old) have notably increased background auto-fluorescence. Arrows indicate sfGFP::SAX-7S expression in neurons of the head (left) or tail (right) ganglia. n ≥ 20 animals examined by confocal microscopy for each stage. z-stack projections. Scale bar, 10 µm.