Figure 5.
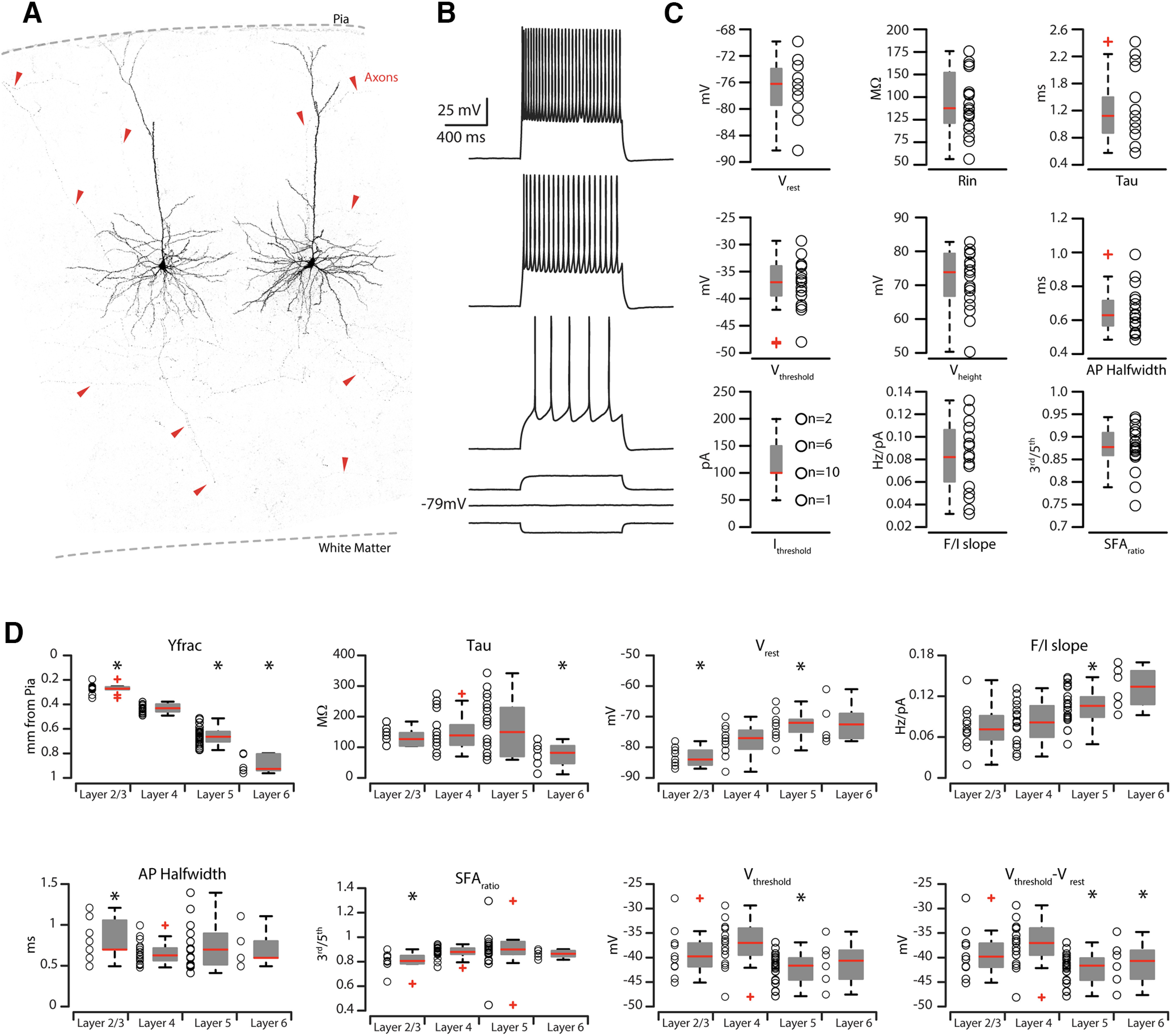
Electrophysiological properties of CS-L4 neurons compared with other corticostriatal neurons in different layers. A, High-resolution confocal images of two biocytin-filled CS-L4 neurons. Red arrowheads point at labeled axons from the two patched cells spanning all layers and going toward the white matter. B, Train of APs recorded in retrograde-labeled CS-L4 neurons during step of current injections (1.0 s, from −50 to 200 pA pulses with increments of 50 pA each step). C, Summary plot of the following: Vrest, resting membrane potential; Rin, input resistance; Tau, membrane time constant; Vthresh, AP threshold voltage; Vheight, AP height; APhalf-width, AP half-width; Ithresh, AP current threshold; F/Islope; SFAratio, AP SFA from CS-L4 neurons (n = 18), including group averages (± SEM). D, Summary plot of the comparison of intrinsic properties of corticostriatal pyramidal neurons across cortical layers. Graphs represent the following: Yfrac, average distance from pia (0); Tau, membrane time constant; Vrest, resting membrane potential; F/I slope; APhalf-width, AP half-width; SFAratio, SFA between third and fifth AP; Vthresh, AP threshold voltage; Vthresh-Vrest, difference between the AP threshold voltage and resting membrane potential from n = 11 CS-L2/3 neurons, n = 18 CS-L4 neurons, n = 15 CS-L5 neurons, and n = 6 CS-L6 neurons, including group averages (± SEM).
