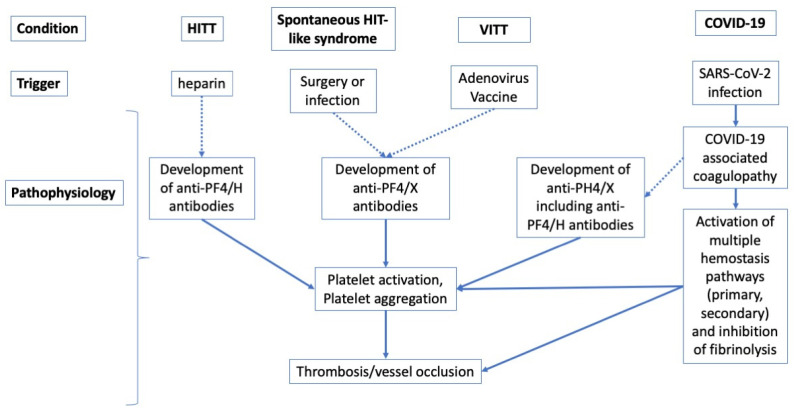
Figure 6.
Navigating the differences and similarities of anti-PF4 antibody development in the different conditions considered in this review. ‘H’ in anti-PF4/H refers to heparin as the PF4 cofactor; ‘X’ in anti-PF4/X refers to a PF4 cofactor that may or may not be heparin. All conditions can lead to the development of anti-PF4 antibodies, which are anti-PF4/H in HITT and in some cases of COVID-19, and which are probably not anti-PF4/H in ‘spontaneous HIT-like syndrome’, in VITT and in a minority of cases of COVID-19. In COVID-19 patients, a generalized infection-associated coagulopathy may develop, in which only rarely will development of anti-PF4/X antibodies occur. Most cases of thrombosis in COVID-19 patients are thus unrelated to the development of anti-PF4/X antibodies.