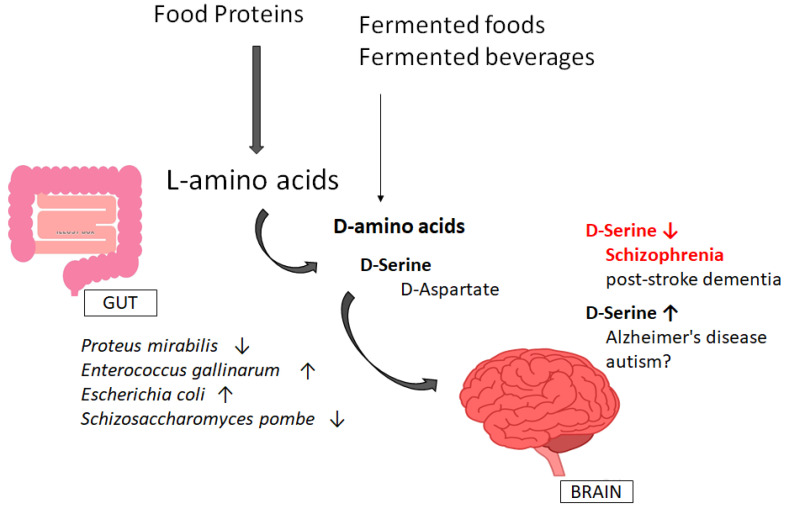
Figure 2.
Gut microbiota might contribute to the creation or the destruction of the D-amino acids, which could play key roles in the pathological processes of psychiatric diseases. The bacteria shown here are instances that are involved in the increase (↑) or decrease (↓) of certain D-amino acid levels. Consequently, decreased levels of D-Serine may be associated with schizophrenia, whereas increased D-Serine levels might be found in Alzheimer′s disease. As a remark, critical events such as ROS production, cytokine induction, and immune activation have been omitted for simplicity.