FIGURE 1. High glucose negatively impacts BK channel function in NHBE cells in vitro.
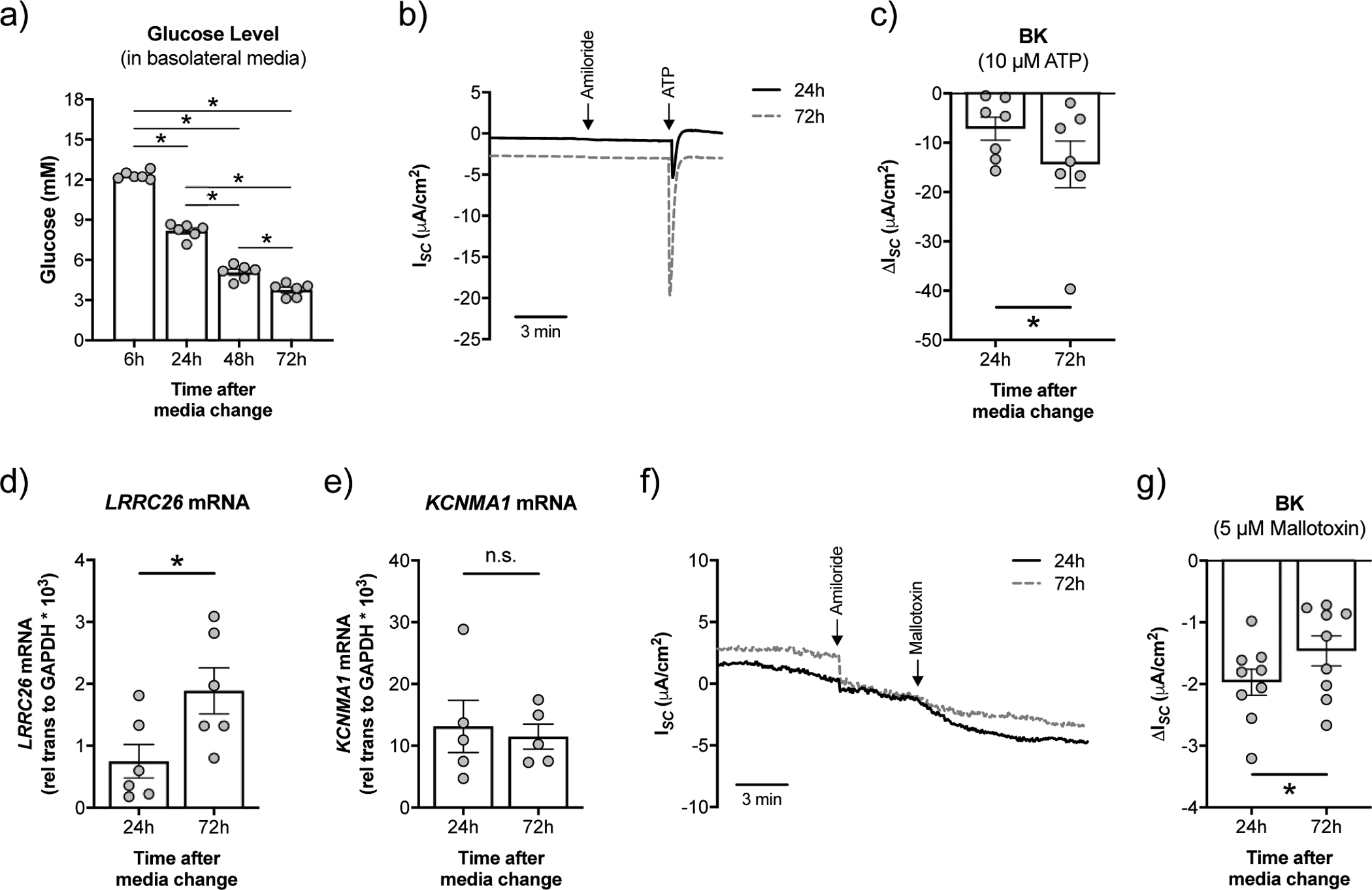
a) Fully differentiated NHBE cells were cultured in ALI media with high glucose (12.5 mM or 225 mg/dL). Measurement of glucose levels in the basolateral media over time (n=6 lungs). * p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s. b) Representative tracing of ATP-stimulated short-circuit current (ISC) measurements in Ussing chambers with a basolateral to apical K+ and apical to basolateral Na+ gradient [34]. ISC is a measure of net ionic current across the epithelium and thus near zero at baseline. c) BK activity is significantly lower at 24 h than at 72 h after media change (n=7 lungs). * p < 0.05, one-tailed t-test. d) mRNA expression levels of LRRC26 correlate inversely with glucose levels (n=6 from 3 lungs). * p < 0.05, unpaired t-test. e) Expression of KCNMA1 mRNA is not significantly different in NHBE cells 24 h and 72 h after media change (n=6 lungs). n.s. = not significant. f) Representative tracing of mallotoxin-stimulated ISC measurements in Ussing chambers with a basolateral to apical K+ gradient [13]. g) Mallotoxin-activated BK is significantly greater in NHBE cells 24 h after media change compared to 72 h (n=9 from 4 lungs). These data indicate that KCNMA1 is still at the plasma membrane and opens with mallotoxin when LRRC26 associations are reduced [13]. * p < 0.05, Student’s t-test. Data are shown as mean ± S.E.M.
