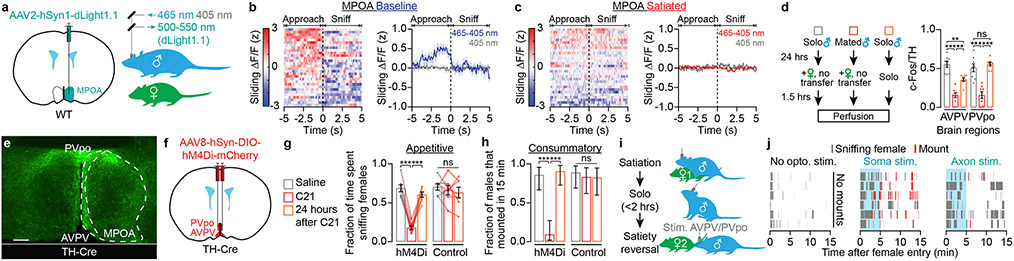
Fig. 2 ∣. Specialized hypothalamic dopamine neurons control mating drive.
a, Two-color photometry of the dopamine sensor dLight1.1.
b, Left: dLight1.1 fluorescence traces aligned to sniff onset, sorted by pre-sniffing dLight1.1 intensity. Right: the average dLight1.1 signal ramped up over seconds as the mouse approached a female, and dropped as the male sniffed the female (n = 6 males). Sliding ΔF/F (z): fractional change in fluorescence, filtered and z-scored.
c, After satiety, dopamine ramps before sniffing were abolished (n = 6 males).
d, In the male AVPV and PVpo, c-Fos is expressed in a lower proportion of TH+ cells following a successful mating (n = 8 males).
e, Axon terminals of AVPV/PVpo dopamine neurons innervate the lateral MPOA (scale bar: 200 μm).
f-h, Bilateral chemogenetic inhibition of male AVPV/PVpo dopamine neurons decreased appetitive sniffing (g: n = 7 males) and consummatory mounting behaviors (h: n = 7, mean ± 95% c.i.).
i-j, Optogenetic stimulation of AVPV/PVpo dopamine neuron cell bodies (‘Soma’) or axons in the MPOA reinvigorates both appetitive sniffing and consummatory mounting behaviors in sexually sated mice. n = 7, 9, 9 males.
Mean ± s.e.m. unless otherwise specified. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. See Supplementary Table 1 for statistics.