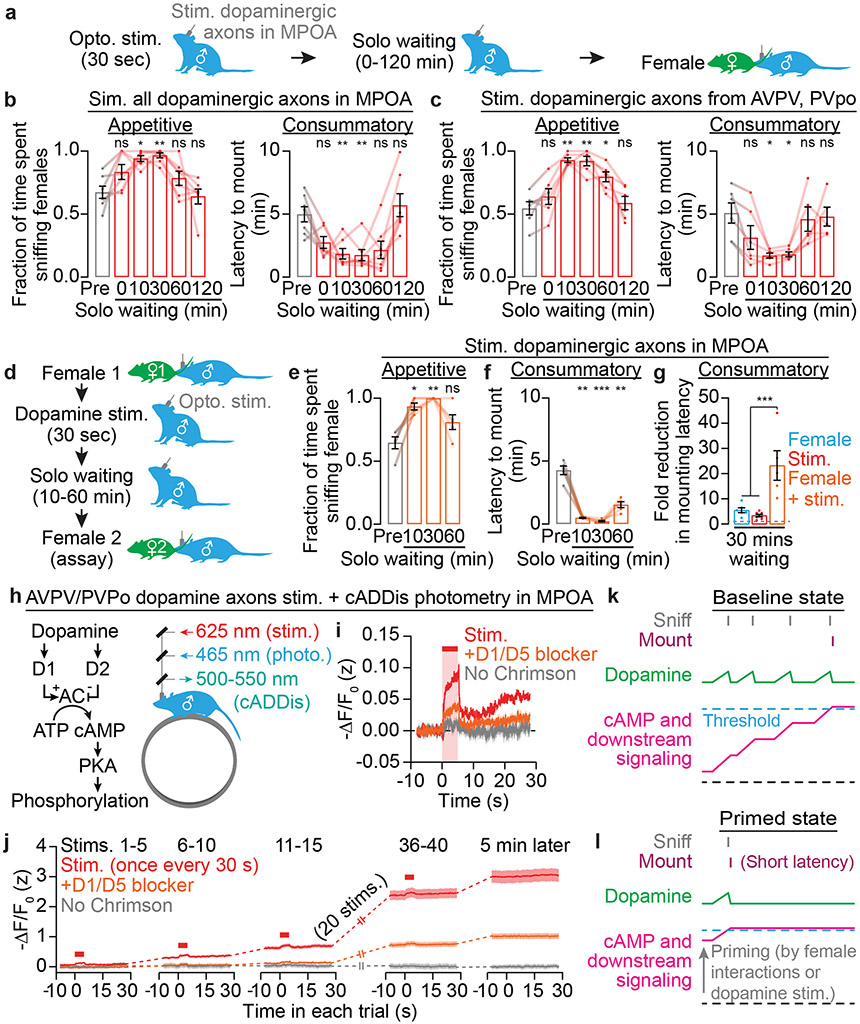
Fig. 3 ∣. Dopaminergic input to the MPOA builds up a persistent motivation to mate.
a-c, Brief optogenetic pre-stimulation (a) of all dopamine axons in the MPOA (b: n = 7 males) or of AVPV/PVpo dopamine axons in MPOA (c: n = 6) led to sustained increases in sniffing behavior and sustained decreases in mounting latency.
d-g, Priming by exposure to a female followed by pre-stimulation of all dopaminergic inputs to the MPOA (d) resulted in increases in appetitive sniffing (e: n = 5 males) and decreases in mounting latency (f: n = 5) that were greater than for either manipulation alone (g: n = 7, 7, 5).
h-j, Dopamine signals through D1- and D2-family receptors to alter cAMP levels and PKA activity (h). Brief Chrimson photostimulation of AVPV/PVpo dopamine axons in the MPOA in vivo (h) triggered local cAMP production (measured by cADDis photometry) that can be attenuated by D1/D5 antagonist SCH23390 (0.6 mg/kg, i.p.) (i: n = 6-7 males). Strikingly, cAMP levels did not completely return to baseline after stimulation but instead accumulated across repeated stimulations and persisted for minutes after the last stimulation (j: n = 6-7). The sign of the Y-axis is flipped, as cADDis fluorescence decreases with increasing cAMP. AC, adenylyl cyclase.
k,l, A model of motivational accumulation. Mean ± s.e.m. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. See Supplementary Table 1 for statistics.