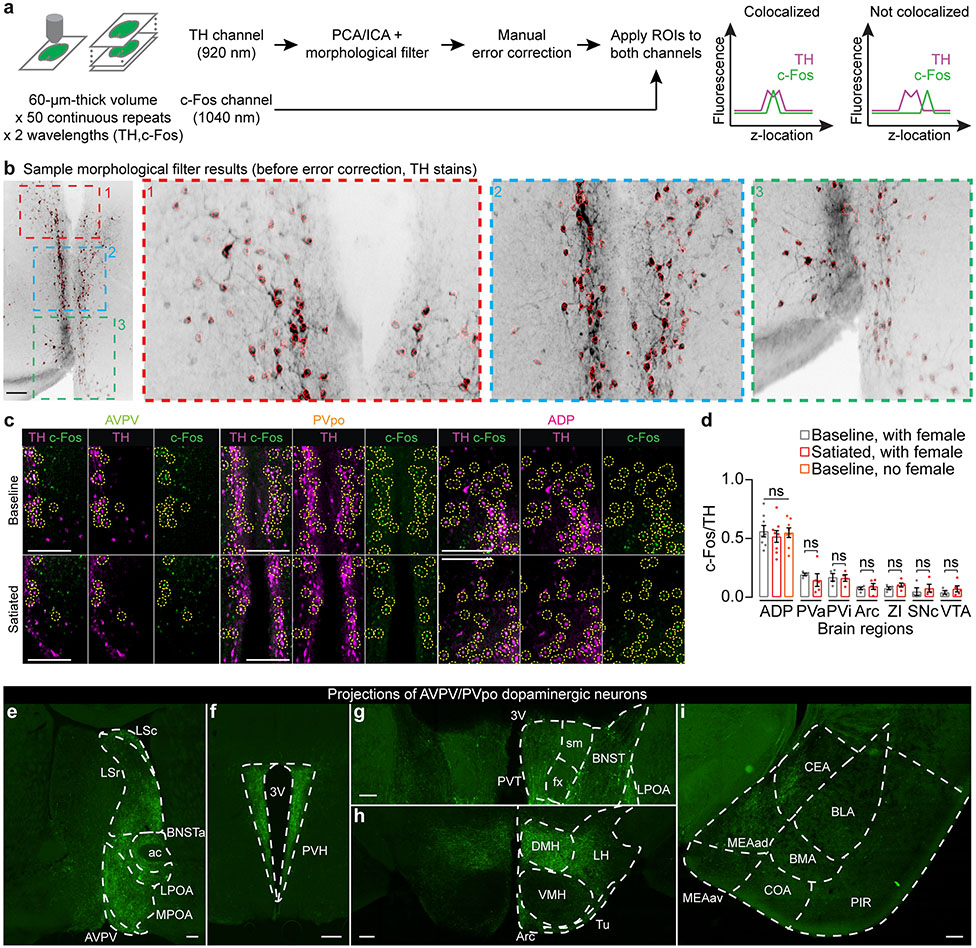
Extended Data Fig. 4 ∣. Dopamine neurons in the AVPV and PVpo nuclei of the hypothalamus.
a,b, Data acquisition and analysis steps for quantifying TH and c-Fos co-localization. Brief description (see Supplementary Methods for details): high-redundancy volumes of 60-μm thick brain slices (50 volumes of 15-30 steps, 2-4 μm/step) that have been stained for TH and c-Fos were collected using a two-photon microscope. To segment dopaminergic somas, we first identified independent components of the TH volume along the z-axis through standard PCA/ICA analysis60. We then applied a morphological filter to the independent components, each usually containing a few closely located cells, to separate the individual somas. The preliminary segmentation results (see b for a sample; scale bar: 200 μm) were then manually corrected and validated before the regions-of-interest (ROIs) were applied to the c-Fos channel. An ROI was considered positive for both TH and c-Fos only if the two intensity profiles (along the z-axis) contained co-localized peaks.
c, Representative images of co-localization of TH and c-Fos in AVPV, PVpo, and ADP. Cells positive for both TH and c-Fos are highlighted with dashed circles (Scale bars: 200 μm).
d, Brain regions that did not show differences in c-fos expression in dopamine neurons (n = 8 males for ADP; 4-5 for all other brain regions; mean ± s.e.m). ADP, anterior dorsal preoptic area; PVa, anterior periventricular nucleus; PVi, intermediate periventricular nucleus; Arc, arcuate nucleus; ZI, zona incerta; SNc, substantia nigra pars compacta; VTA, ventral tegmental area.
e-i, Projections of AVPV/PVpo dopamine neurons (identified by injecting Cre-dependent axon-GCaMP6s in unilateral AVPV/PVpo of a TH-Cre male). Note that no axons were observed in the basolateral amygdala, which receives strong mesolimbic dopamine inputs. 3V, third ventricle; ac, anterior commissure; Arc, arcuate hypothalamic nucleus; BLA, basolateral amygdala nucleus; BMA, basomedial amygdala nucleus; BNST, bed nucleus of stria terminalis; BNSTa, anterior bed nucleus of the stria terminalis; CEA, central amygdala nucleus; COA, cortical amygdala area; DMH, dorsomedial nucleus of the hypothalamus; fx, column of fornix; LPOA, lateral preoptic area; LSc, caudal lateral septum; LSr, rostral lateral septum; MEAad, anterodorsal medial amygdala nucleus; MEAav, anteroventral medial amygdala; PIR, piriform area; PVH, paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus; PVT, paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus; sm, stria medullaris; Tu, tuberal nucleus; VMH, ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus. Scale bars: 200 μm.