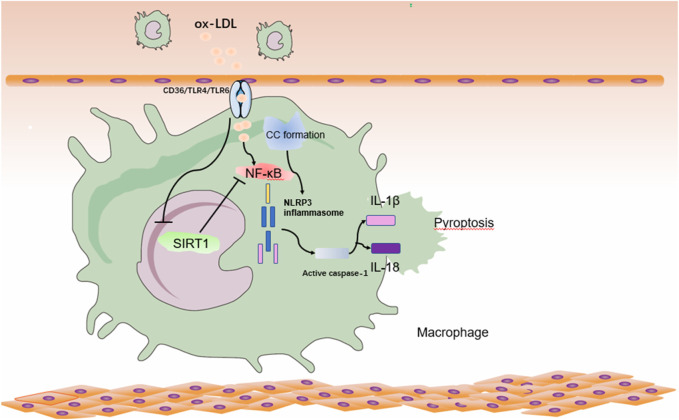
FIGURE 2.
Relationship between SIRT1 and pyroptosis pathway in atherosclerosis in macrophages. Ox-LDL and CC- in atherosclerotic lesions activates NF-κβ in macrophages with NLRP3 inflammatory vesicle initiation and NLRP3 inflammatory vesicle activation, promoting the inflammatory factor IL-18/IL-1β, leading to cytoplasmic swelling and membrane rupture, resulting in the release of inflammatory factors and promoting the onset of pyroptosis. At the same time, ox-LDL inhibits the expression of SIRT1, which further leads to the activation of NF-κβ, and this vicious circle will further aggravate the development of AS. ox-LDL: oxidatively modified low-density lipoprotein; NF-κβ: nuclear factor kappa-light chain-enhancer of activated B.