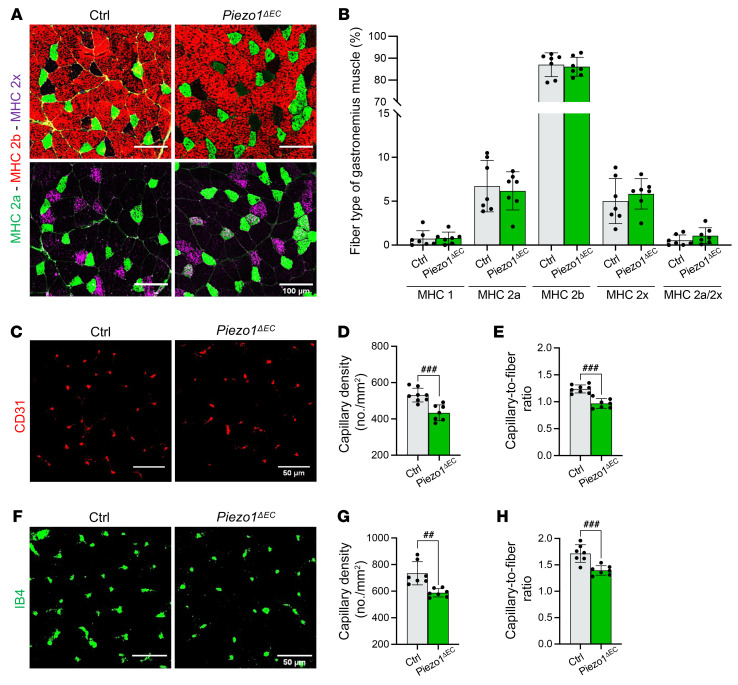
Figure 2. Endothelial Piezo1 specifically affects microvascular density.
(A) Immunohistochemistry of gastrocnemius muscle cross sections for myosin heavy chain (MHC) type 2a (green) plus type 2b (red, left) or type 2x (magenta, right). Scale bars: 100 μm. (B) Quantification of the relative frequency of the different fiber types in gastrocnemius muscle. (C) Immunohistochemistry for CD31 (red) to visualize endothelial cells in capillaries of gastrocnemius muscle sections. Scale bars: 50 μm. (D) Mean data for capillary density measured from images of the type shown in C. (E) Similar to D but showing mean data for the ratio of capillaries to muscle fibers. (F) Immunohistochemistry for isolectin B4 (IB4, green) to visualize endothelial cells in capillaries of gastrocnemius muscle sections. Scale bars: 50 μm. (G) Mean data for capillary density measured from images of the type shown in F. (H) Similar to G but showing mean data for the ratio of capillaries to muscle fibers. All data are for n = 7 to 8 mice per group (mean ± SD). Superimposed dots are the underlying data values for each individual mouse. Gray indicates muscles from Ctrl mice and green indicates muscles from Piezo1ΔEC mice. ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs. ctrl mice. Statistical significance was evaluated using Student’s t test.