Figure 1.
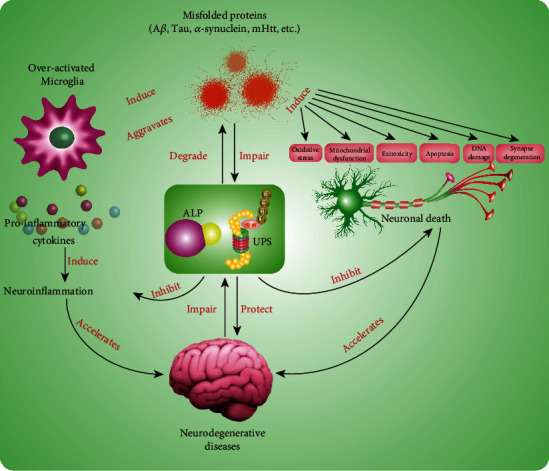
The role of misfolded proteins in neurodegenerative diseases. The misfolded proteins, including Aβ, Tau, α-synuclein, and mHtt, induce the overactivation of microglia and neuronal death. The overactivated microglia release the amount of proinflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, IL-1β, IL-18, and TNF-α, and then induce neuroinflammation. Meanwhile, the overactivation of microglia aggravates the aggregation of misfolded proteins. Neuronal death was induced by misfolded proteins through multiple mechanisms, including oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, excitotoxicity, apoptosis, DNA damage, and synapse degeneration. Both neuroinflammation and neuronal death accelerate the progress of neurodegenerative diseases. However, both ALP and UPS acting as two major degradation pathways not only clear the misfolded proteins but also inhibit neuroinflammation and neuronal death in the early stage of neurodegenerative diseases. However, the overaccumulation of misfolded proteins and degenerated brain impair the normal function of ALP and UPS.
