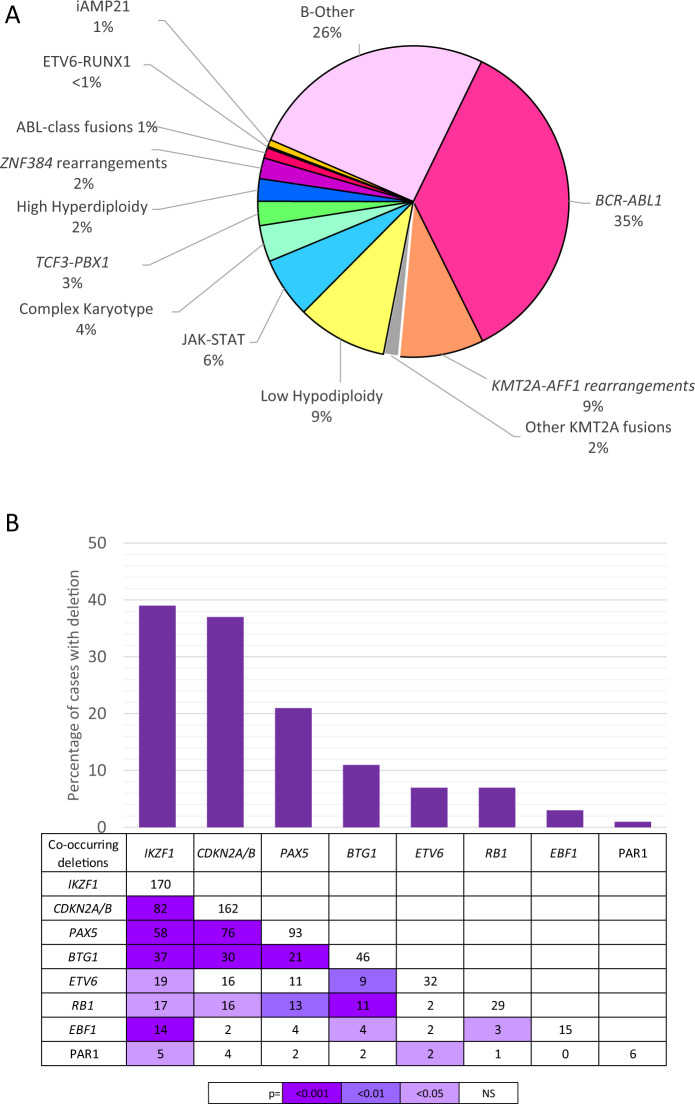
Fig. 1. Frequency of primary chromosome abnormalities (A) and secondary copy numbers alterations (B) in adults with B-cell precursor ALL enroled to UKALL14.
A Pie chart showing the frequency of chromosomal abnormalities. Most KMT2A rearranged cases had KMT2A-AFF1 (i.e., t(4;11), 49/58, 84%) but other partner genes were observed: MLLT1 (n = 6) and MLLT4, EPS15, LASP1, unknown (one each). The low hypodiploidy (30–39 chromosomes) group included two cases of near-haploidy (26–28 chromosomes). The JAK-STAT group comprised IGH-CRLF2 (n = 23), P2RY8-CRLF2 (n = 9) and JAK2 fusions (n = 2, PAX5-JAK2 & BCR-JAK2). P2RY8-CRLF2 fusions were identified by MLPA (n = 4), FISH (n = 3) or both techniques (n = 2). We were able to identify the partner gene in 3/6 cases: EBF1-PDGFRB (n = 2), FOXP1-ABL1 (n = 1). The remaining three cases had a PDGFRB/CSF1R (n = 2) or ABL1 (n = 1) rearrangement. Twelve patients had a ZNF384 rearrangement with EP300 (n = 5) and TCF3 (n = 4) being the most prevalent partners along with single cases of AKAP8-ZNF384 and EWSR1-ZNF384 and one where the partner gene is unknown. B Bar chart and table showing the frequency and co-occurrence of copy number alterations.