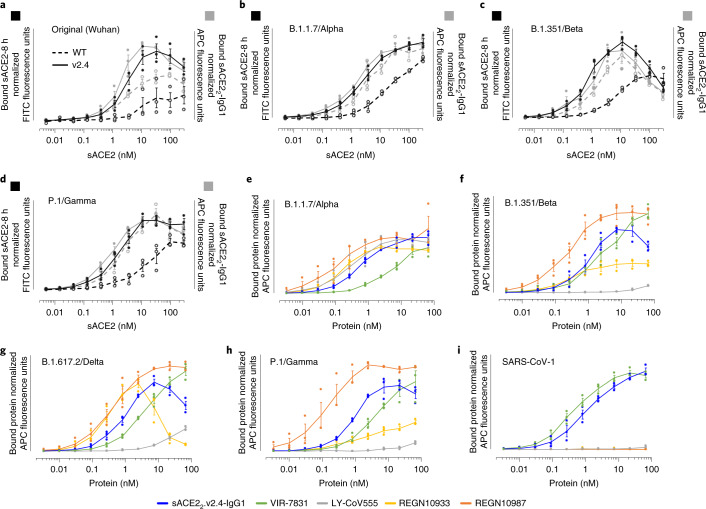
Fig. 5. ACE2 decoys carrying the v2.4 mutations bind the S protein from multiple highly transmissible SARS-CoV-2 VOCs and SARS-CoV-1.
a–d, sACE2 carrying the v2.4 mutations has increased S binding compared with WT sACE2. Human Expi293F cells expressing myc-tagged S from 4 SARS-CoV-2 variants (Wuhan (a), B.1.1.7/Alpha (b), B1.351/Beta (c) and P.1/Gamma (d)) were incubated with monomeric sACE2-8 h (black) or dimeric sACE22-IgG1 (gray); bound protein was detected by flow cytometry. WT ACE2 proteins are shown as broken lines, v2.4 proteins are shown as solid lines. n = 3 independent replicates; data are shown as the mean ± s.e.m. e–i, Binding of sACE22.v2.4-IgG1 is comparable to clinically effective mAbs. Binding of mAbs versus sACE22.v2.4-IgG1 to the S proteins of SARS-CoV-2 VOCs (B.1.1.7/Alpha (e), B1.351/Beta (f), B.1.617.2/Delta (g) and P.1/Gamma (h)) and S protein of SARS-CoV-1 (i), as measured by flow cytometry. n = 3 independent replicates; data are shown as the mean ± s.e.m.