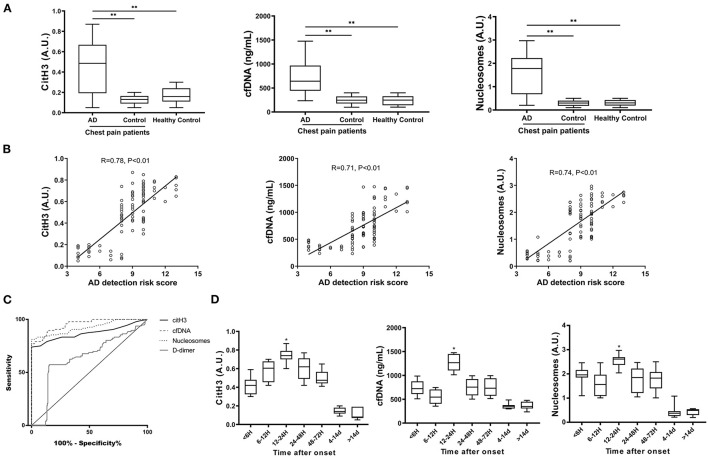
Figure 1.
The diagnostic performance of circulating NET markers for discriminating AAD. (A) Serum levels of citrullinated H3 (citH3), cell-free DNA (cfDNA), and nucleosomes were evaluated in 96 patients with AAD and 249 patients in the control group. CitH3 and nucleosomes are expressed in arbitrary units (AU). The cfDNA concentration (ng/mL) was determined based on a calibration curve of calf thymus DNA. All three markers were significantly higher in the AAD group than in the control group. (B) Serum levels of citH3, cfDNA and nucleosomes were positively correlated with the detection risk score of AD. (C) ROC curve for the diagnosis of AAD. Circulating NET markers showed superior overall diagnostic performance compared with D-dimer when sudden-onset chest pain was present in the emergency department. (D) The time course of NET markers was examined in patients with AAD according to the admission time from symptom onset. The peak NET marker levels occurred within 12–24 h of symptom onset. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.