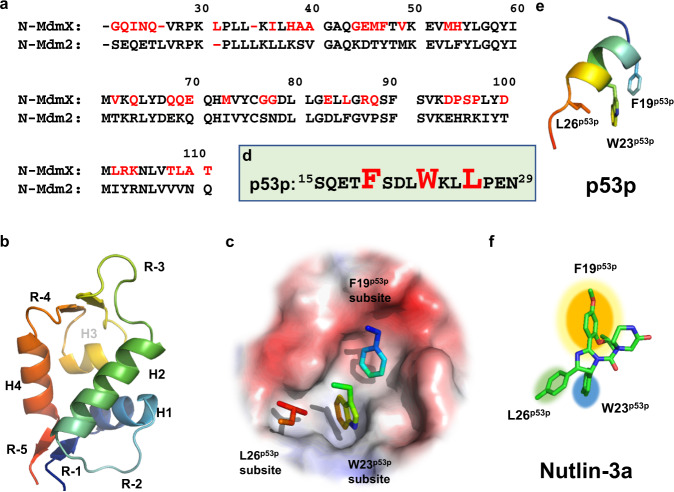
Fig. 1. Three subsites on N-MdmX and N-Mdm2 are defined by three key binding residues of p53p.
a Alignment of the amino acid sequence of N-MdmX with that of N-Mdm2. Non-identical residues on N-MdmX are shown in red. b A cartoon model representing N-MdmX and N-Mdm2 structures, based on their crystal structures in complex with p53p. c Each ligand-binding pocket on N-MdmX or N-Mdm2 is composed of three subsites, i.e., the F19p53p, W23p53p, and L26p53p subsites, with reference to the three key binding residues of p53p. d The amino acid sequence of the p53p peptide. Three key residues, i.e., F19p53p, W23p53p and L26p53p, are in red. e The structure of p53p with three key residues highlighted. f Nutlin-3a can be docked tightly into the three subsites on N-Mdm2, mimicking p53p.