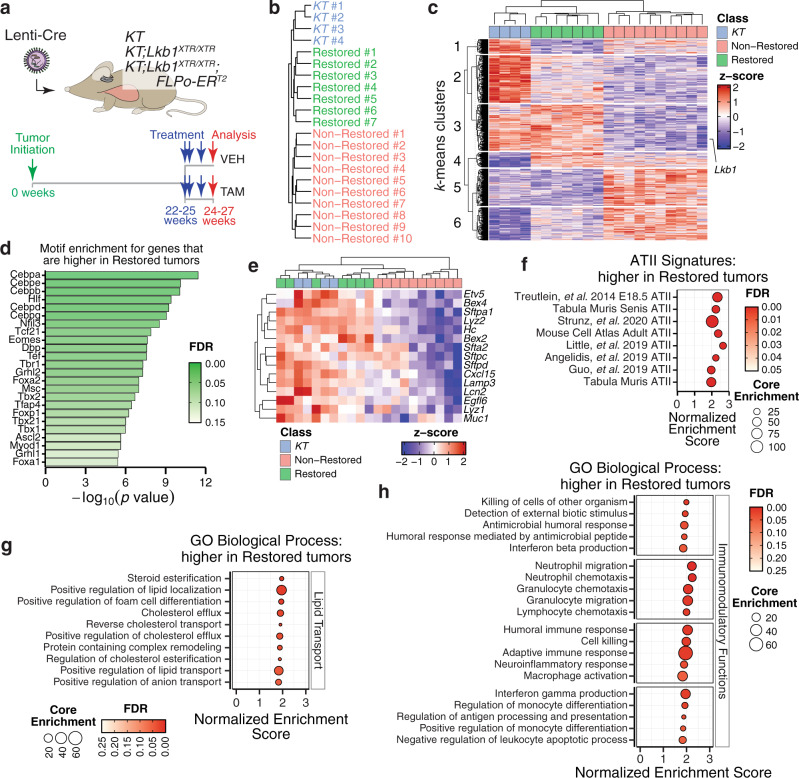
Fig. 3. Lkb1 restoration drives programs related to alveolar type II epithelial cell functions in lung adenocarcinoma.
a Profiling the acute transcriptional response to Lkb1 restoration within established lung tumors. Mice were treated with vehicle or tamoxifen for 2 weeks prior to fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS)-isolation of tdTomatopositive neoplastic cells for RNA-seq analysis. KT, n = 4 mice; KT;Lkb1XTR/XTR-tamoxifen, n = 3 mice; KT;Lkb1XTR/XTR;FLPo-ERT2-vehicle, n = 3 mice; KT;Lkb1XTR/XTR;FLPo-ERT2-tamoxifen, n = 4 mice. VEH vehicle, TAM tamoxifen. b Hierarchical clustering of the transcriptional profiles of Lkb1 wild-type (KT), non-restored, and restored tumors by Euclidean distance. c Heatmap of genes that vary significantly (FDR < 0.05; likelihood ratio test). Lkb1 is indicated. K-means clustering defined sets of genes that change concordantly across all samples (left). d Transcription factor motifs enriched within the putative promoters (−450 to +50 bp from transcription start site) of those genes that are higher (log2 Fold Change >1 and FDR < 0.05) in restored lung tumors relative to non-restored using the JASPAR 2018 collection of position frequency matrices. e Expression of markers associated with alveolar type II epithelial cell identity across Lkb1 wild-type, non-restored, and restored tumors. f–h GSEA using signatures of ATII identity derived from previously published single-cell RNA-seq datasets (f) and the Gene Ontology (GO) Biological Process module (g, h), illustrating the enrichment of gene sets among those genes that are higher in restored relative to non-restored tumors. Groups of enriched gene sets relating to lipid metabolism and transport (g) as well as immunomodulation (h) are shown. The size of the dots corresponds to the number of core enrichment genes and the fill color reflects FDR.