Figure 2. Acute SCI alters different neuroinflammatory pathways between male and female.
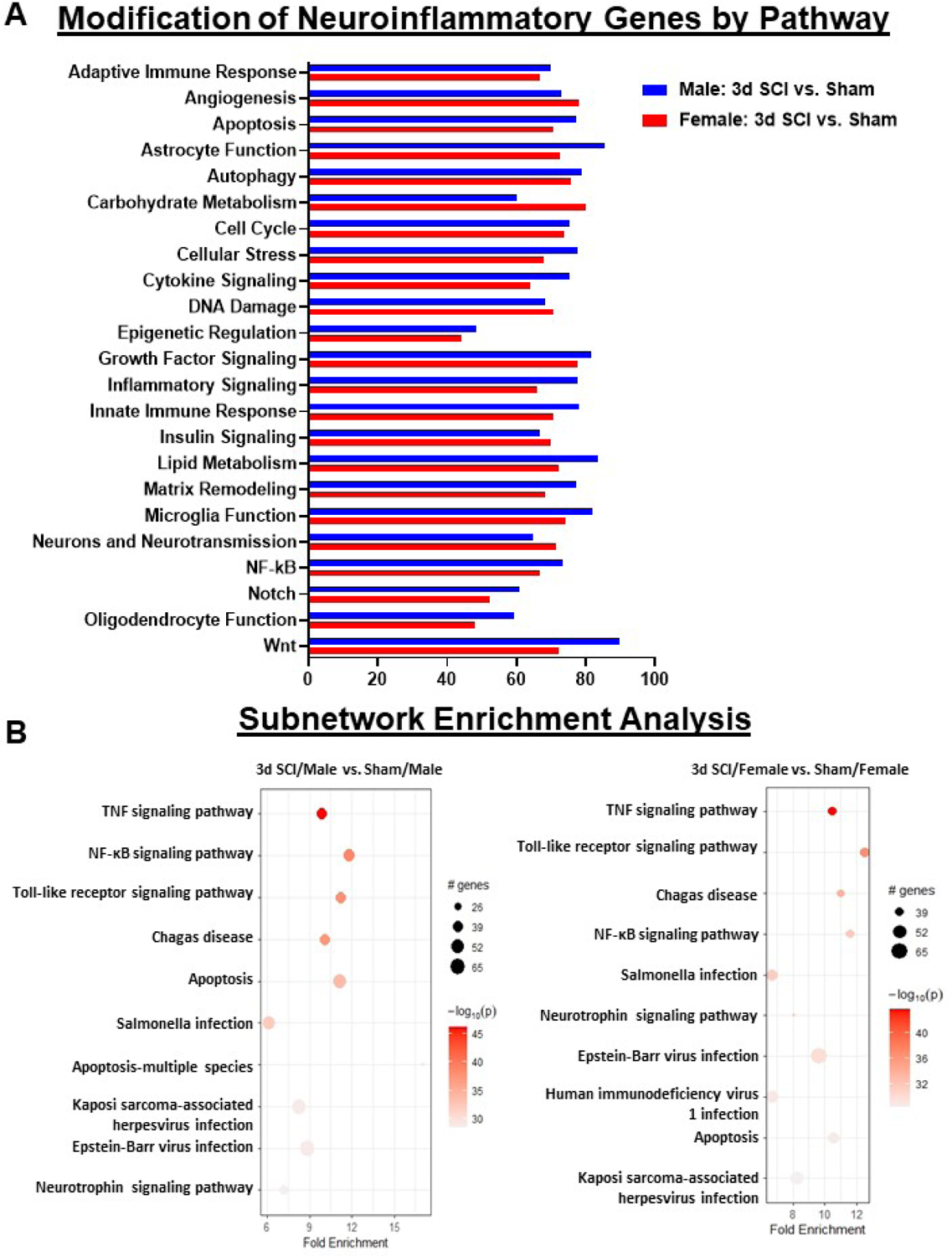
(A) Graph illustrating the neuroinflammatory genes altered by spinal cord injury in different sexes. Injury genes in male mice indicated higher alteration in Astrocyte Function, Cellular Stress, Cytokine Signaling, Inflammatory Signaling, Lipid Metabolism and Wnt Signaling pathway. Female mice indicated higher levels of alteration in Angiogenesis, Carbohydrate Metabolism, DNA Damage and Neurotransmission. (B) Sub-network enrichment analysis with Rstudio’s PathfindR package shows more significant enrichment of genes related to NF-kappaB and Apoptosis Signaling pathway in male mice after injury, while female mice showed higher alterations to Toll-like Receptor and Neurotrophin Signaling pathways. N=3–4 mice/group.
