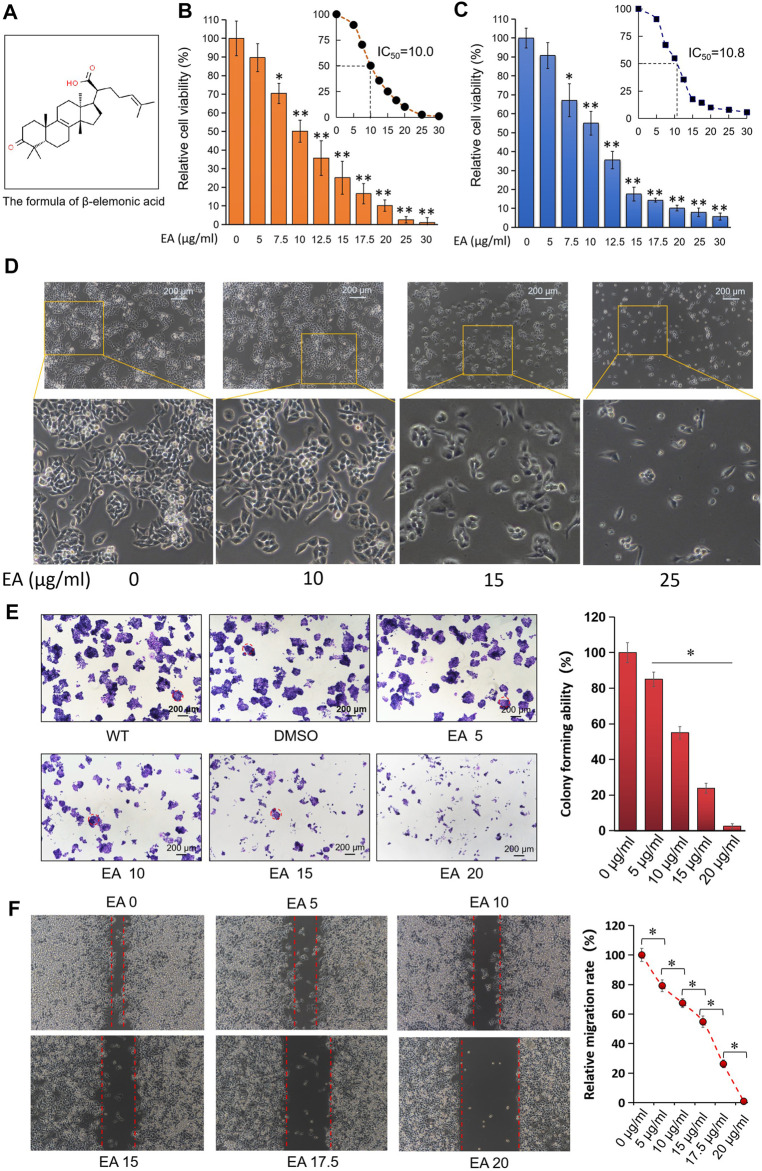
FIGURE 1.
EA inhibited colorectal cancer cells in dose-dependent manner in vitro. (A) The formula of β-elemonic acid (EA); (B) Colorectal cancer SW480 cells were co-incubated in different concentrations of EA for 48h, and the cell activity was detected by the CCK8 kit. Four independent experiments were performed. The difference was calculated by a two-way t-test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (C) Colorectal cancer HCT116 cells were co-incubated in different concentrations of EA for 48 h, and the cell activity was detected by the CCK8 kit. Four independent experiments were performed. The difference was calculated by a two-way t-test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (D) SW480 cells were treated by EA for 48 h. And the EA-caused morphological changes in SW480 cells were photographed with an inverted microscopy. (E) 6 × 102 SW480 cells were cultured into 12-well plates, and the cells were treated with different concentrations of EA for 10 days. The cell colonies were stained with crystal violet. The colonies with a diameter up to 200 μm were involved into the statistical comparison (see right column figure). The difference was calculated using a one-way ANOVA analysis, *p < 0.05. (F) The inhibitory effect of EA on the migration of colorectal cancer cells was examined by scratch assay. SW480 cells were co-incubated with 0–20 μg/ml EA for 24 h, and then the scratch width was measured. The scratch width was measured by ImageJ software. The rate of closure of cell scratches was quantified and shown in the right inset. Three independent experiments were performed. The difference was calculated by a two-way t-test, *p < 0.05.