Figure 5. Glutamate imaging in the OPL.
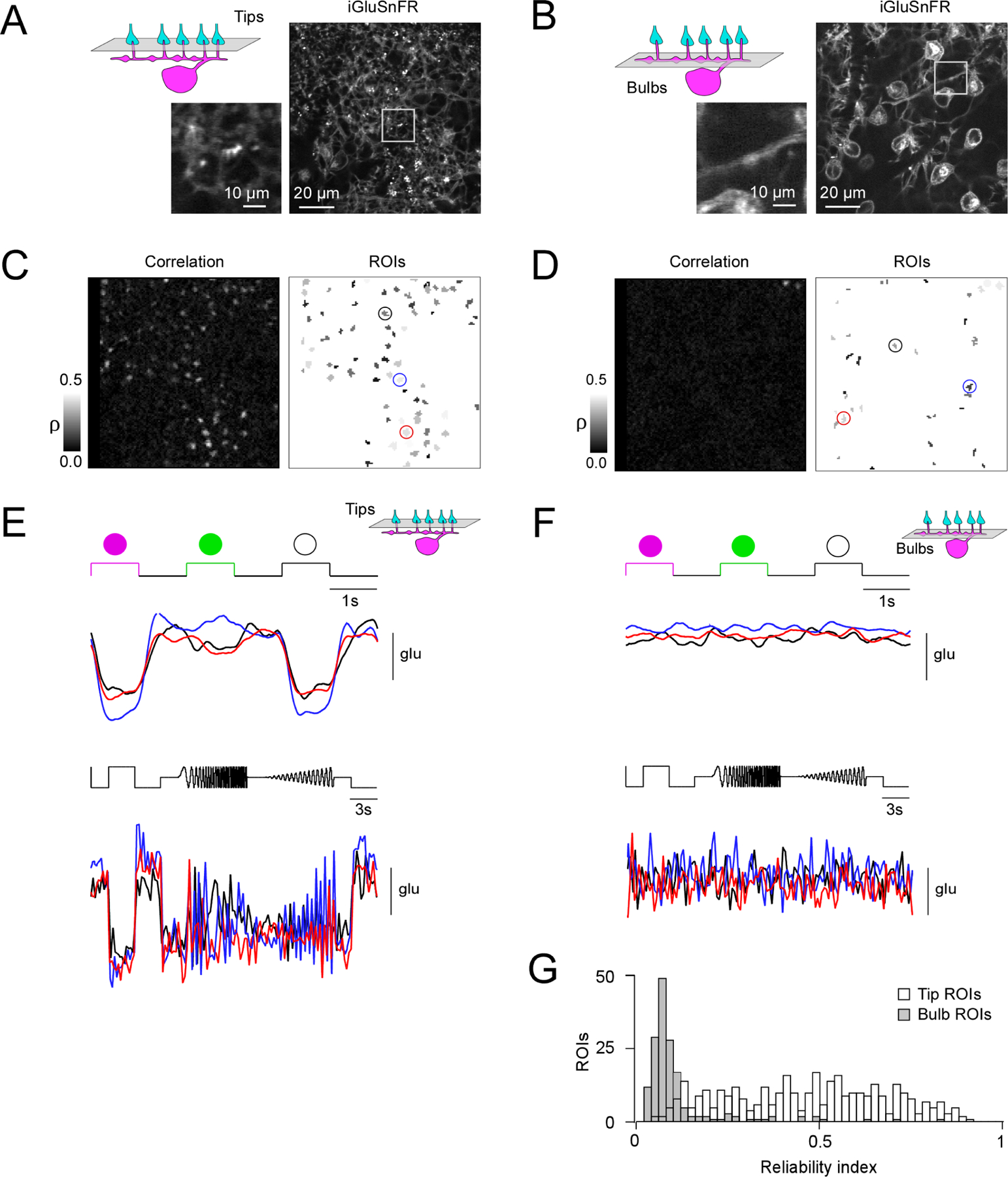
(A, B) Horizontal scans of a Cx57cre/+ transgenic mouse retina in which HCs express the fluorescent glutamate sensor iGluSnFR after intravitreal AAV injection (see STAR Methods), with the focal plane in the OPL at the level of the HC tips (A) and at the level of the HC primary dendrites (B). (C) Correlation image (left) indicating hotspots of light-evoked glutamate release at HC tips and resulting regions-of-interest (ROIs; right). (D) Like (C) but at the primary HC dendrite level. Note that a lower correlation threshold was used than in (C) to draw ROIs (see STAR Methods). (E, F) Light-evoked glutamate signals (top, UV-green-white flashes; bottom, local chirp) are only detectable in the plane of the HC tips (E) but not at bulbs (F). (G) Histogram of reliability indices of UV-green-white flash responses for all ROIs (n = 359 at tip level, white bars; n = 166 at bulb level, grey bars) in n = 6 scan fields and n = 3 mice. P < 0.05; two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test. For complemental axial (x-z) scans see Figure S4.
