Figure 1. Membrane fatty acid composition‐dependent growth of B. subtilis and E. coli .
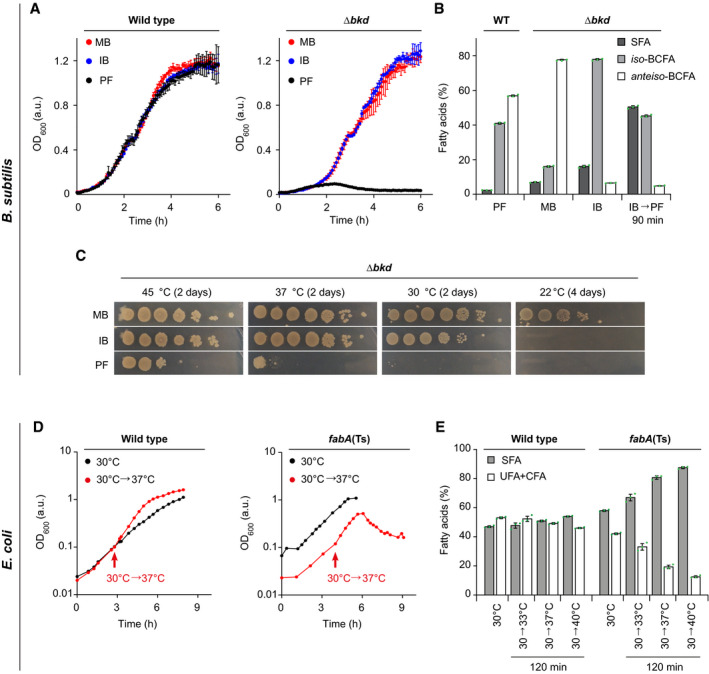
- Growth of B. subtilis WT and fatty acid precursor‐auxotrophic Δbkd cells in medium supplemented with precursor 2‐methyl butyric acid (MB), isobutyric acid (IB) or grown precursor‐free (PF).
- Fatty acid composition of B. subtilis WT cells grown in PF medium, and Δbkd grown with MB, IB or depleted for precursor for 90 min (IB→PF). For detailed analyses, see Appendix Fig S1B.
- Temperature‐dependent growth of B. subtilis Δbkd on solid medium in serial 10‐fold dilutions. For comparison between WT, Δdes and Δbkd Δdes cells, see Appendix Fig S1C.
- Temperature‐dependent growth behaviour of E. coli WT and fabA(Ts), including a shift from 30 to 37°C as non‐permissive temperature of fabA(Ts).
- Fatty acid composition of E. coli WT and fabA(Ts) cells grown at 30°C and shifted to different temperatures for 120 min. For detailed analyses, see Appendix Fig S2B and C.
Data information: (A) The diagram depicts mean and standard deviation (SD) of technical triplicates for each strain. (B, E) The histograms depict mean and SD of biological triplicates. (C, D) The experiments are representative of three independent repeats. CFA, cyclopropane fatty acid. Strains used: (A–C) B. subtilis 168, HS527; (D, E) E. coli MG1, MG4 (strains Y‐Mel and UC1098, respectively, additionally encoding fluorescent ATP synthase (FOF1 a‐mNG)).
Source data are available online for this figure.
