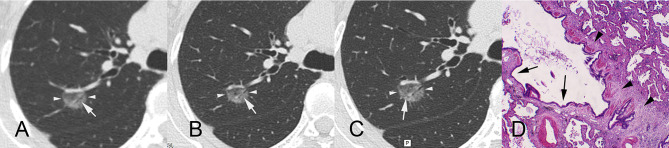
Figure 3.
A 55-year-old female patient with ground-glass nodules in the posterior segment of the right upper lobe detected by LDCT screening. AI indicated that the malignant rate was 97.46%. Surgical resection revealed invasive mural adenocarcinoma. CT images reconstructed by lung window. (A) LDCT image. The white arrow indicates that there is an obscure air bronchogram in the nodule. (B) Conventional CT image. The white arrow indicates a slightly clear air bronchogram in the nodule. (C) HRCT local-target scanning image. An abnormal air bronchogram is visible. The white arrow indicates that the target scan shows a finer tortuous bronchial sign. (D) Pathological HE staining image (×40) showing diffuse tumour tissue around bronchioles, infiltration and growth of tumour tissue, and proliferation of fibrous connective tissue (arrowheads), resulting in bronchiectasis (arrows). AI, artificial intelligence; LDCT, low-dose computed tomography; CT, computed tomography; HRCT, high-resolution computed tomography.