Figure 5.
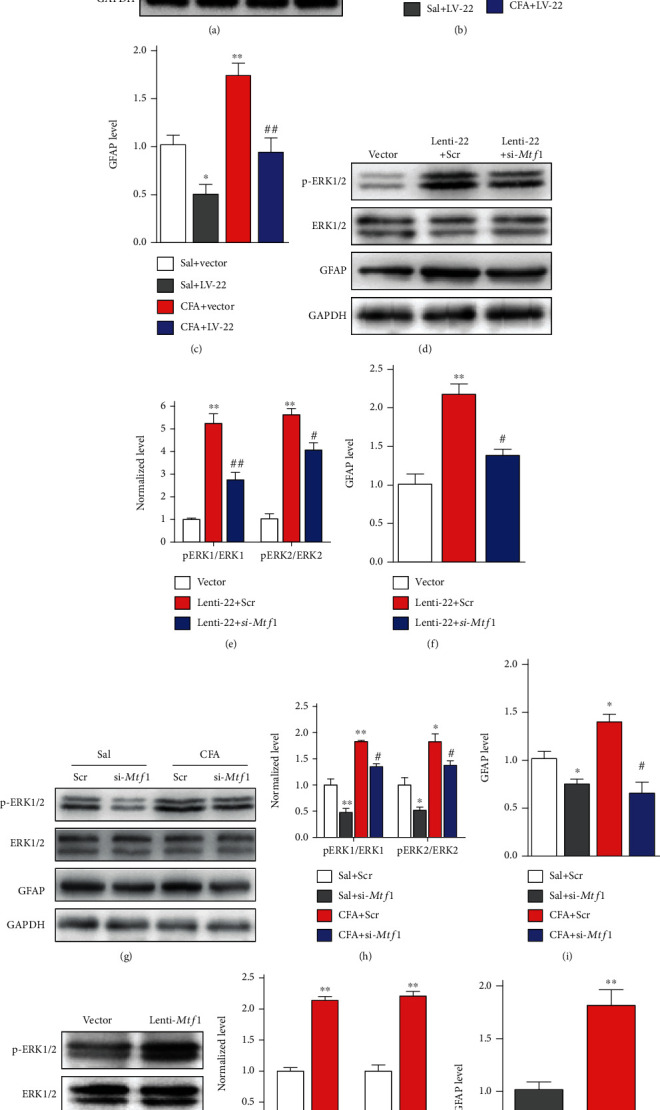
miRNA-22 activates ERK1/2 via regulation of Mtf1. (a)-(c) Knockdown of miRNA-22 with LV-22 reversed the CFA-induced increase in p-ERK1/2 (a, b) and GFAP protein (c) in the dorsal horn. ∗p <0.05, ∗∗p <0.01 versus Saline+Vector. n =5. ##p <0.01 versus CFA + Vector. n =5. Data were analyzed with a two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey test. (d)-(f) miRNA-22 overexpression induced by Lenti-22 enhanced the protein levels of p-ERK1/2 (d, e) and GFAP (f) in naïve mice, and this increase was inhibited by Mtf1 knockdown with si-Mtf1. Tissues were harvested on day 2 after si-Mtf1 following intrathecal injection of Lenti-22. ∗∗p <0.01 versus Vector. #p <0.05, ##p <0.01 versus Lenti-22 + Scr. n =5. Data were analyzed with a one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey test. (g)-(i) siRNA-induced Mtf1 knockdown weakened the CFA-induced increase in p-ERK1/2 (g, h) and GFAP (i) protein. ∗p <0.05, ∗∗p <0.01 versus Sal+Scr. n =5. #p <0.05 versus CFA + Scr. n =5. Data were analyzed with a two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey test. (j)-(l) Intrathecal injection of Lenti-Mtf1 increased the expression of p-ERK1/2 (j, k) and GFAP (l) protein in naïve mice. ∗∗p <0.01 versus Vector. n =5. Data were analyzed with a Student's t test.
