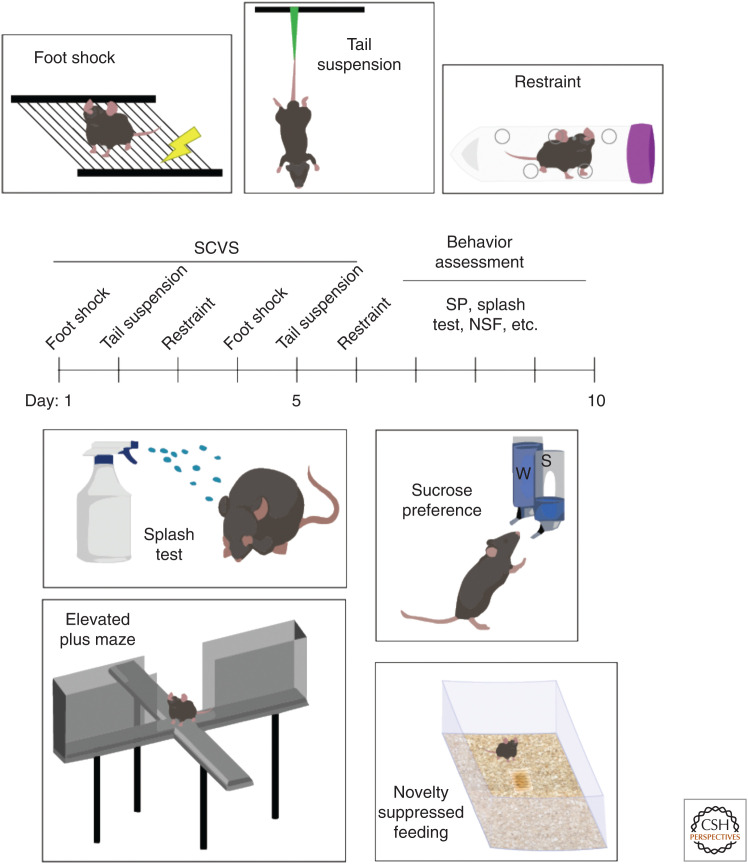
Figure 2.
Subchronic variable stress (SCVS) and associated behavioral assays. SCVS comprises a 6-d battery of repeated stressors (top): foot shock, tail suspension, and restraint stress. Each stress session typically lasts 1 h per day. Following the stress period, a variety of behavioral assays are used to assess stress susceptibility (bottom): splash test, sucrose preference (SP), elevated plus maze (EPM), novelty suppressed feeding (NSF), and social interaction ([SI], not pictured). Splash test measures grooming behavior, with susceptible animals showing reduced grooming time when sprayed with a sticky solution. Sucrose preference indicates anhedonic response with two-bottle choice task, with susceptible animals showing no preference for sucrose drinking solution. EPM measures anxiety response, with “anxious” animals spending less time in open arms and more time in closed arms of the apparatus. Novelty suppressed feeding represents a more subtle measure of anxiety, with “anxious” animals exhibiting increased latency to eat (following overnight food deprivation) in a novel environment.