Fig. 4.
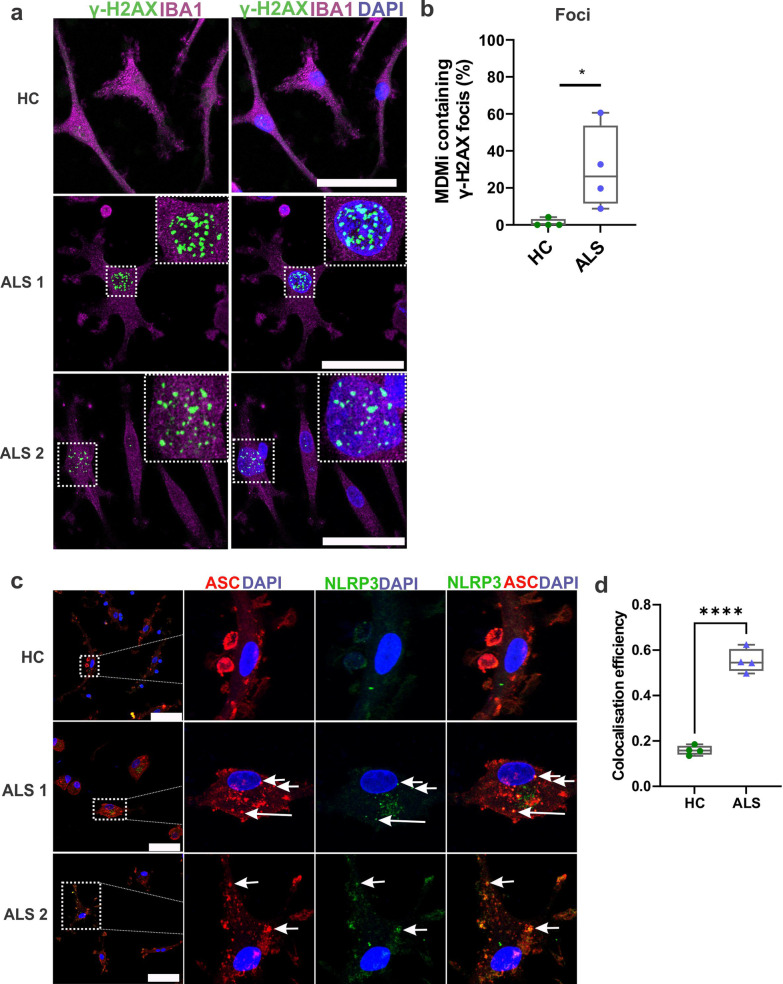
ALS MDMi display DNA damage and NLRP3 inflammasome formation. a Representative immunofluorescence images of ALS MDMi showing γH2AX (green), Iba1 (magenta), and DAPI counterstain (blue). Enlarged images on the top right indicates γH2AX foci in ALS MDMi. b Increased percentage of MDMi containing γH2AX foci in ALS (n = 4) compared to HC MDMi (n = 4, Day14). 60 cells per individual. Formula is as follows (number of cells containing γH2AX foci / total number of cells)*100. c Representative immunofluorescence images of HC and ALS MDMi showing NLRP3 (green), ASC (red) and DAPI counterstain (blue). NLRP3 in HC (top panel) does not co-localise with ASC, while ASC speck was co-localised with NLRP3 in ALS MDMi suggesting inflammasome formation. d Colocalisation (Pearson’s colocalisation efficiency) between NLRP3 and ASC in HC and ALS MDMi. HC: n = 4, ALS: n = 4, 10 cells per individual. All HC and ALS MDMi cultures were differentiated for 14 days and were unstimulated. Data were first tested for normality using Shapiro–Wilk test. Statistical analysis between two groups was performed using Student’s t test. ASC: apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD; NLRP3: NLR family pyrin domain containing 3. Values are mean ± SD (*P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001). Scale bars = 50 µm