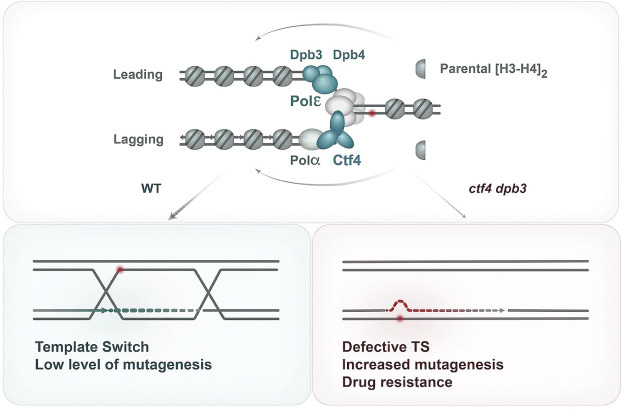
Figure 7.
Model representing the regulating roles of histone transfer pathways on the usage of error-free versus error-prone pathways of DNA damage tolerance. (Top) Schematics showing that Dpb3–Dpb4 and Mcm2–Ctf4–Polα facilitate parental (H3–H4)2 transfer to the leading and lagging strands of the replication fork. (Bottom) In WT cells, error-free and error-prone pathways are correctly balanced to favor error-free template switching and exclude TLS polymerases from the nascent strands. When Dbp3–Dpb4 and Mcm2–Ctf4–Polα pathways of parental histone transfer are defective, the error-free branch of DDT is impaired and TLS polymerases have increased access to the nascent strands, leading to increased mutagenesis and drug resistance.