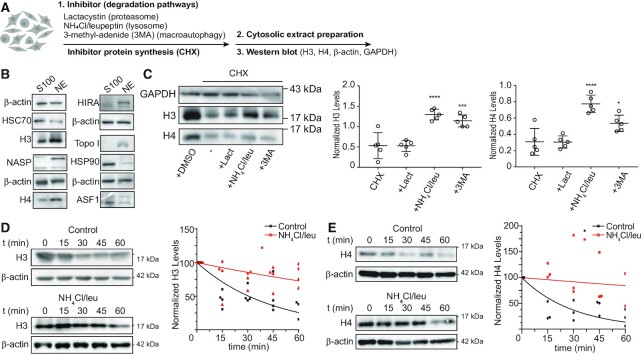
Figure 1.
Newly synthesized histones H3 and H4 are degraded by lysosomes. (A) Scheme illustrating the experimental approach to assessing cytosolic H3 and H4 levels after the inhibition of different protein degradation pathways on HeLa cells. Cells were pre-incubated for 10 min with 10 μM Lactacystin, 20 mM NH4Cl + 200 μM leupeptin, and 10 mM 3-MA, followed by 1 h treatment with 100 μg/ml CHX in the presence of the inhibitors. (B) Western blot analyses of 5 μg of cytosolic (S100) and nuclear (NE) extracts derived from HeLa cells. (C) Left, representative immunoblot of 5 μg of cytosolic extract. Graph shows normalized levels of cytosolic H3 (left) and H4 (right) by GAPDH signal on each condition. N = 5 independent experiments; *P-value < 0.05, ***P-value < 0.001, ****P-value < 0.0001, Student's t-test. (D, E) Left, HeLa cells were pre-incubated with or without 20 mM NH4Cl + 200 μM leupeptin for 10 min before addition of 100 μg/ml CHX. Cytosolic extracts were prepared at 0, 15, 30, 45 and 60 min after treatment and analyzed by western blot for H3 (D) and H4 (E). Right, histone H3 (D) and H4 (E) signal was quantified by densitometry and normalized against β-actin. Mean values obtained from 4 (H3) and 3 (H4) independent experiments were adjusted to a non-linear regression (first-order exponential decay).