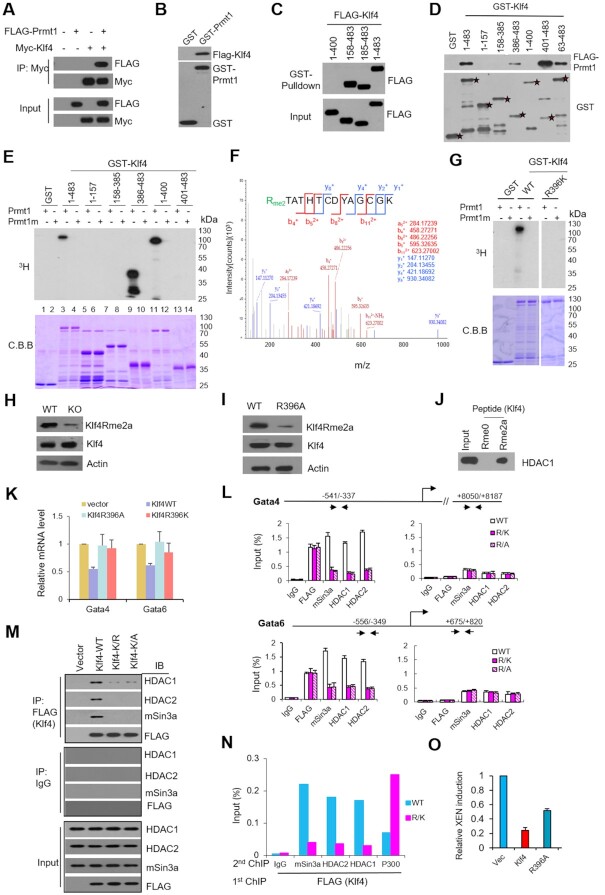
Figure 4.
Klf4 methylated by Prmt1 at R396 is involved in the expression of PrE genes. (A) Co-IP of Prmt1 and Klf4. Whole-cell extracts (WCEs) of HEK293T cells transfected with (+) or without (–) Myc-Klf4 and/or FLAG-Prmt1 were subjected to IP with an anti-Myc antibody and blotted with antibodies specific for FLAG for Prmt1 and Myc for Klf4. (B) GST pulldown assays to detect the interaction of Prmt1 with Klf4. GST or GST-Prmt1 was incubated with WCEs of HEK293T cells expressing FLAG-Klf4 and then blotted with antibodies specific for FLAG or GST. (C) Purified GST-Prmt1 was incubated with WCEs of HEK293T cells expressing FLAG-Klf4 and its truncations. The GST pulldown products were immunoblotted with an anti-FLAG antibody, and WCEs that were not subjected to IP were used as the input. (D) Purified GST-Klf4 and its derivatives were incubated with WCEs of HEK293T cells expressing FLAG-Prmt1 or vector. The GST pulldown products were then immunoblotted with an anti-FLAG antibody for Prmt1 or an anti-GST antibody. (E) Autoradiography of in vitro methylation assays using purified GST-Klf4 and its derivatives with Prmt1 or Prmt1m (an inactive enzymatic mutant). Total amounts of GST-Klf4 and Klf4 truncations were visualized by Coomassie brilliant blue (C.B.B.) staining. (F) MS analysis of a Klf4 peptide mixture to identify methylated sites in vitro. Dimethylated arginine (Rme2) is displayed in green. (G) Autoradiography of in vitro methylation assays using purified GST-Klf4 and an R396K mutant of Klf4 with Prmt1 or Prmt1m. (H) Western blotting assay with anti-Klf4R396me2a, Klf4, and Actin in E14 ES cells (WT) and Prmt1 KO cells. (I) Western blotting assay with anti-Klf4R396me2a, Klf4, and Actin in AB2.2 ES cells without (WT) or with R396A mutation of Klf4 (R396A). (J) Peptide pulldown assay with purified HDAC1 by unmethylated peptide of Klf4 (Rme0) or asymmetric di-methylated peptide of Klf4 (Rme2a). (K) RT-qPCR analysis showed the effects of Klf4-WT, Klf4-R396A, Klf4-R396K and vector on the expression levels of Gata4 and Gata6 in E14 cells. (L) ChIP assays showed the recruitment of mSin3a, HDAC1, and HDAC2 to the promoters of Gata4 and Gata6 in E14 cells transfected with Klf4 (WT) or Klf4 point mutants at R396 (R/K or R/A). (M) Co-IP assays of Klf4 with the mSin3a complex. WCEs of E14 cells transfected with FLAG-Klf4 (WT) or its R396 mutants (Klf4-R/K or Klf4 R/A) were subjected to IP with an anti-FLAG antibody and then blotted with antibodies specific for HDAC1, HDAC2, mSin3a and FLAG for Klf4. WCEs that were not subjected to IP were used as the input. IgG was used as a negative control. (N) ChIP/re-ChIP assays showed that Klf4-mediated mSin3a/HDAC recruitment to the promoter of Gata6 is arginine methylation dependent. E14 cells were transfected with FLAG-Klf4 (WT) or its mutant at R396 (R/K). An anti-FLAG antibody was used for the initial ChIP (first) to obtain the Klf4-associated chromatin fragments. Then, these fragments were subjected to re-ChIP (second) using mSin3a, HDAC1, and HDAC2 antibodies. IgG was used as a ChIP control. (O) FACS showed the impact of mutant R396 of Klf4 in E14 cells transfected with Klf4 and its mutants R396A and R396F. The percentage of Gata6+/Nanog− cells is shown.