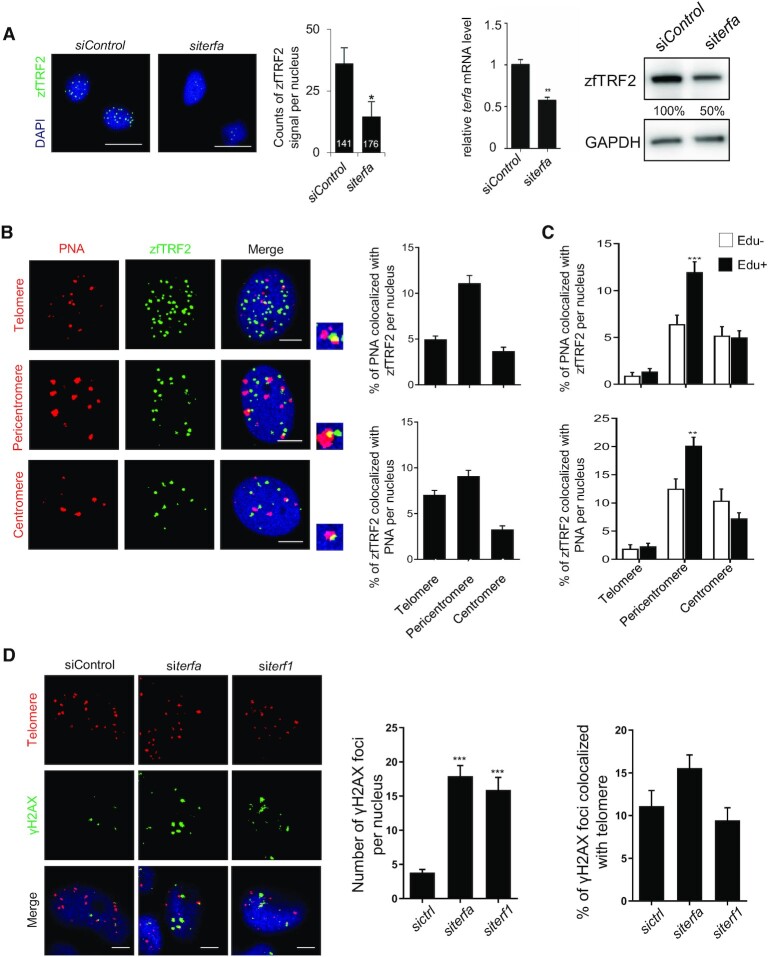
Figure 1.
zfTRF2 downregulation leads to genome-wide DNA damage response with no telomere-specificity. (A) Representative image and quantification of immunofluorescence (left) and immunoblot (right) of zfTRF2 signal to identify the affinity of the purified anti-zfTRF2 antibodies for zfTRF2 in ZF4 cells following TERFA downregulation by siRNA. The number inside the column of the graph indicates the total number of nuclei was counted in three biological replicates. The knockdown efficiency of siRNA was validated by RT-qPCR. Scale bars, 20 μm. (B) Representative images and quantification of immunofluorescence of PNA probe(red) for telomeres (top), pericentromeres (middle) and centromeres (bottom) colocalizing with zfTRF2 (green) in ZF4 fish cells. (C) The percentage of the signals of PNA probes colocalized with zfTRF2 and percentage of zfTRF2 signals colocalized with PNA were shown in ZF4 cells classified by Edu + and Edu- with immunofluorescence assay. (D) Representative images and signal quantification of global and telomere-associated γH2AX foci in ZF4 fish cells upon terf1 and terfa downregulation. Scale bars, 7 μm. Data are shown as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of at least three biological replicates. For immunofluorescence and confocal section images, at least 30 nuclei were taken and counted in each sample for each biological replicate. Statistical analyses were performed using unpaired two-sided t tests (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).