Fig. 1. Genetic mapping of an anti-silencer element in mature CD4 T cells.
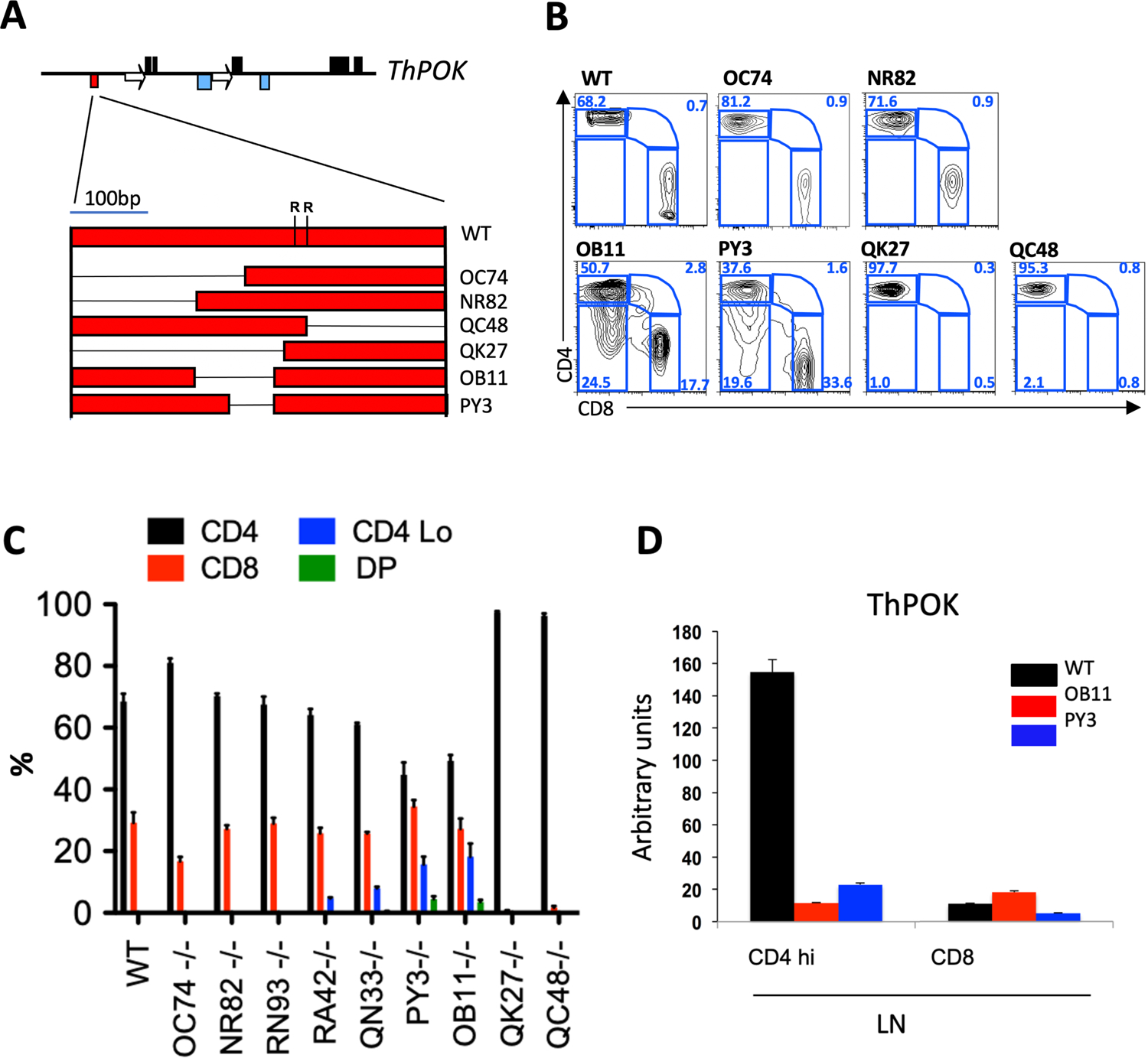
a) Organization of mouse ThPOK gene (top), and diagram of silencer deletion mutants (bottom). Black boxes, blue boxes, arrows, and red boxes indicate exons, enhancers, silencers and promoters, respectively. Deletions within the silencer are indicated by thin black lines. “R” indicates positions of conserved Runx binding sites. b) FACS analysis of CD4, and CD8a expression in gated TCRβ+ PBLs of WT mice and homozygous mutant lines, as designated in panel a. c) Plots indicate % of SP CD4, CD8, CD4+ 8+ (DP) and CD4lo/− cells within gated TCRβ+ PBLs of indicated strains (n = 5, for each strain). Error bars represent standard deviations. d) RNA was collected from freshly isolated cells before probing for ThPOK expression by qPCR.
