Figure 1. Therapeutic targets in Alzheimer’s disease signaling.
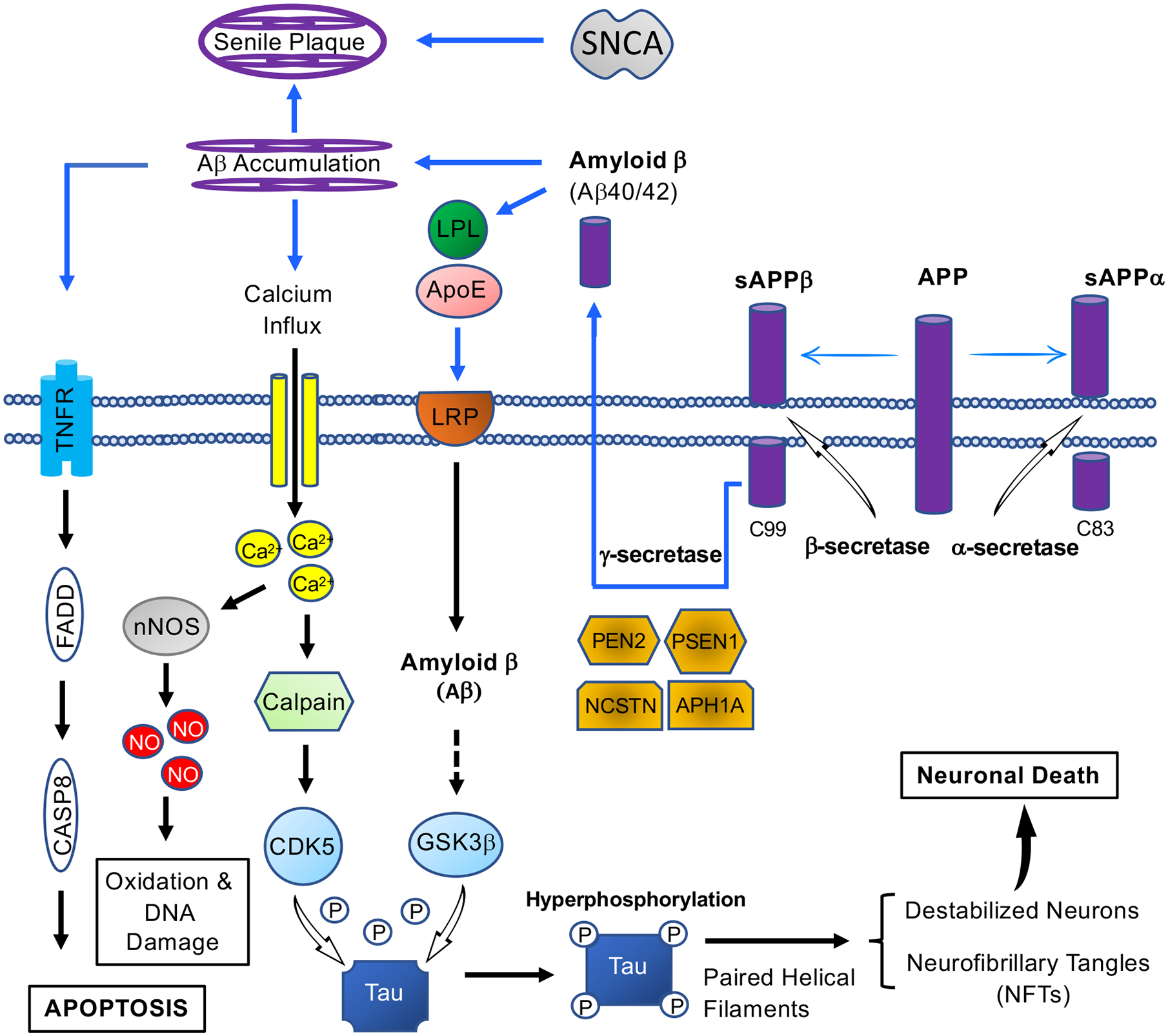
The formation of NFTs and senile plaques in AD signaling introduces several therapeutic targets. Four genes are pathogenetically committed to AD: amyloid precursor protein (APP), apolipoprotein E (ApoE), presenilin 1 (PSEN1) and presenilin2 (PSEN2). An increased level of amyloid-beta peptides is caused by mutations in APP and PSEN, leading to the formation of amyloid-beta 42, the main component of senile plaques. Cleavage of APP either by alpha-secretase or beta-secretase initiates extracellular release of soluble APP peptides, sAPPα and sAPPβ, and retains the corresponding membrane-anchored C-terminal fragments, C83 and C99. Alternatively, PSEN1/Nicastrin (NCSTN)-mediated gamma-secretase processing of C99 releases the amyloid-beta proteins, Amyloid β (Aβ40/42). In neuronal cell bodies, neurite outgrowth is stimulated by ApoE-containing lipoprotein lipase (LPL), via interacting with and letting LRP to bind APP for production of proteolytic fragment (Aβ) [161]. The accumulation Amyloid β results in blocked ion channels, mitochondrial oxidative stress, and activation of TNFR-regulated Caspase 8, and ultimately neuronal cell death. On the other hand, GSK-3 phosphorylates Tau at several sites for partial inhibition of tau biological activity in AD [162]. Upon abnormal Ca2+ homeostasis disturbance, the stimulation of calpain mediates the cleavage of p35 to p25 for the activation of CDK5, leading to hyperphosphorylation of Tau, and also promotion of APP truncation [163]. Finally, the elevated Ca2+ stimulates neuronal NO synthase, leading to production of nitrogen species and reactive oxygen [164]. SNCA: Alpha synuclein; PEN2: Presenilin Enhancer (Gamma-Secretase Subunit); APH1A: Aph-1 Homolog A (Gamma-Secretase Subunit); TNFR: Tumor necrosis factor receptors; FADD: Fas-associated protein with death domain; CASP8: Caspase 8; nNOS: Neuronal nitric oxides synthase
