Fig. 3.
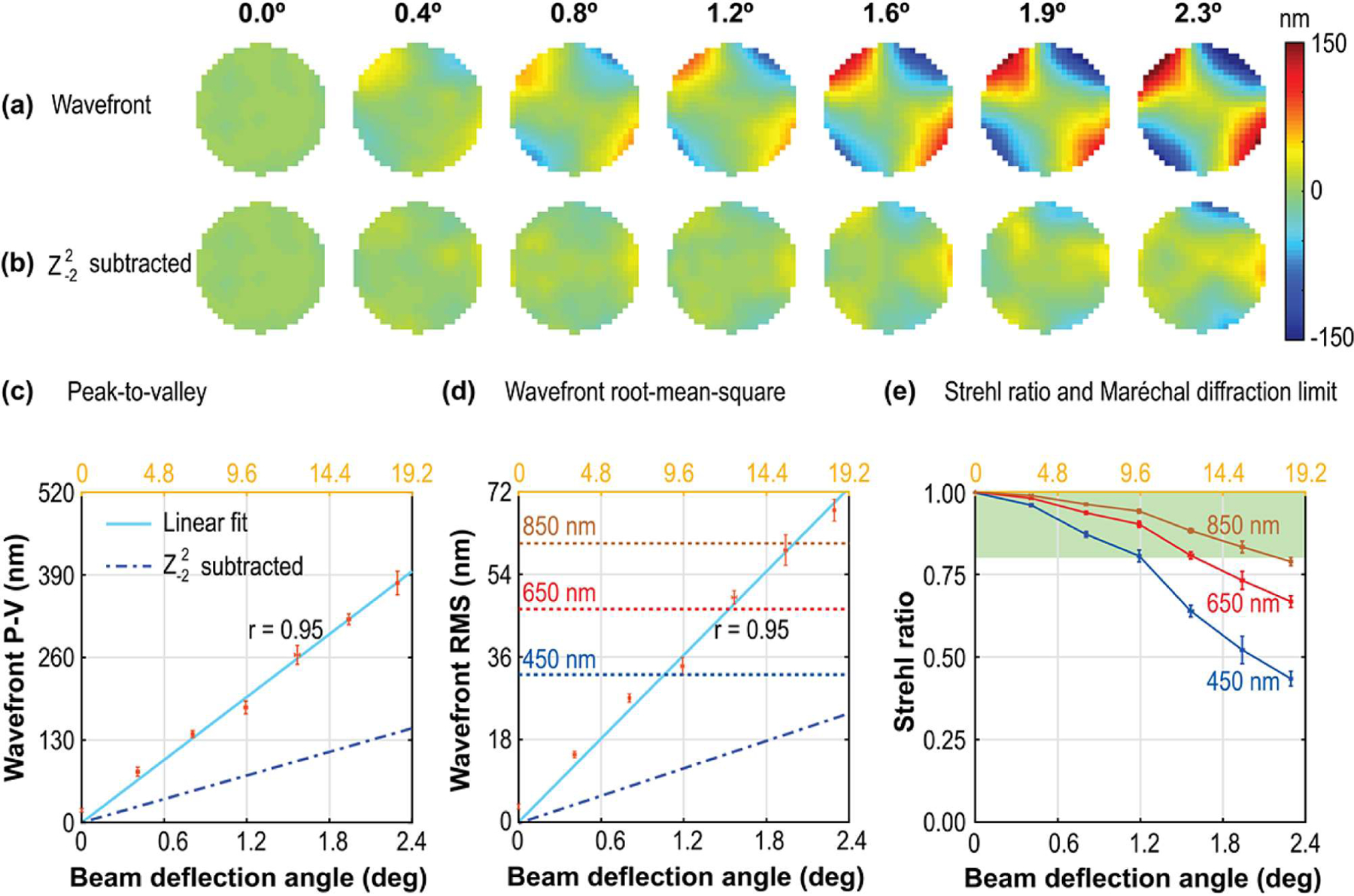
Dynamic wavefront distortions at various deflection angles in a galvanometric resonant scanner with a SiC mirror oscillating at 13.8 kHz and over a 4 mm clear aperture diameter, (a) Full wavefront, and (b) after oblique astigmatism subtraction; (c) and (d) show the linear increase of wavefront P-V and RMS with beam deflection angle. The dotted lines parallel to the x axis in (d) represent diffraction-limited RMS for the corresponding wavelengths. The Strehl ratio as a function of the beam deflection angle at 450, 650 and 850 nm wavelengths is shown in (e), and the green shaded region satisfies Maréchal diffraction-limited performance. The values along the top horizontal axes in light orange denote the Lagrange invariant (product of maximum peak-to-peak beam deflection angle and beam diameter) in units of millimeters/degrees to facilitate performance comparison with other scanners.
