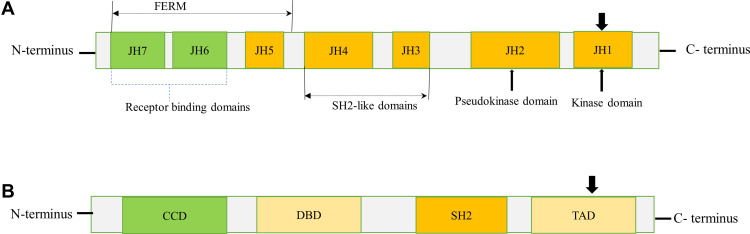
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of JAK and STAT structures. (A) JAKs contain a FERM domain (400 amino acid residues) that associates with receptors, a SH2 domain (100 amino acid residues) that binds phosphorylated tyrosine residues, and a kinase (JH1) domain (250 amino acid residues) and pseudo kinase (JH2) domain (300 amino acid residues). The arrowhead pointed downward (JH1) indicates phosphorylation sites (tyrosine residues) needed for JAK activation. (B) STATs contain a CCD for dimerization, a DBD, a SH2 domain, and a TAD for transcriptional activation of target genes. The arrowhead pointed downward (TAD) indicates the conserved tyrosine residue required to be phosphorylated for STAT activation. N and C represents the amino- and carboxy-terminal ends respectively.
Abbreviations: CCD, coiled-coil domain; DBD, DNA-binding domain; FERM, four-point-one, ezrin, radixin, moesin; TAD, transactivation domain.