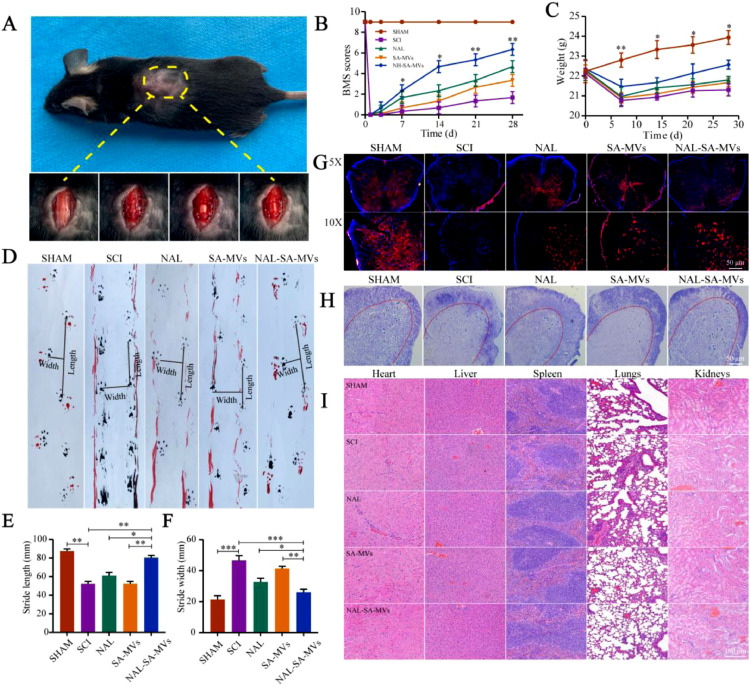
Fig. 8.
NAL-SA-MVs could promote the survival of neurons and the recovery of motor function in mice after spinal cord injury, and the evaluation of the preparation safety. (A) The wound surface of a mouse in the process of SCI model. (B) Statistical analysis of BMS scores in different groups before and after spinal cord injury in mice. (C) Statistical analysis of body weight of mice before and after spinal cord injury. (D) Footprints of SHAM, SCI, NAL, SA-MVs and NAL-SA-MVs group. The forepaws and hindpaws of each group were stained, respectively, with black and red dye. (E, F) The statistical analysis of step length (SL) and stride width (SW). (G) Neun-labeled neurons at 5 × and 10 × of the different groups. (H) Number of surviving neurons at 7d after spinal cord injury in each group by Nissl staining. (I) HE staining of heart, liver, spleen, lung and kidney tissue sections of each group for safety evaluation. All data represented the mean ± SD (n = 5). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.