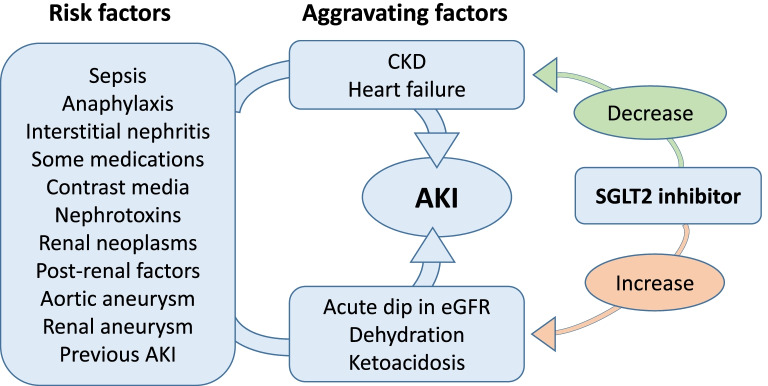
Fig. 3.
Schematic diagram to show the potential effects of SGLT2 inhibition on acute kidney injury (AKI). Use of an SGLT2 inhibitor is not a recognised risk for the occurrence of AKI, and available evidence indicates that SGLT2 inhibitors may be associated with a reduced occurrence of AKI. SGLT2 inhibitors may alter factors that ‘aggravate’ the severity of AKI. For example, SGLT2 inhibitors might improve the prognosis for people with AKI by decreasing the rate of decline of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) in people with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and by reducing the severity of heart failure. SGLT2 inhibitors might impair the prognosis for people with AKI if the SGLT2 inhibitor has been started recently and there is a drug-induced dip in eGFR and by dehydration or ketoacidosis