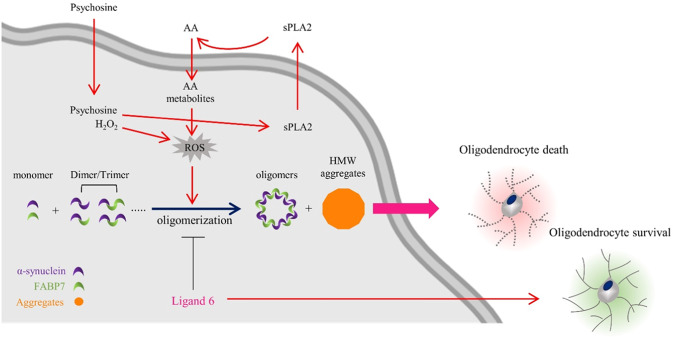
Fig. 7. Schematic representation of the pathways through which FABP7 triggers αSyn oligomerization associated with oxidative stress and induces oligodendrocyte loss.
During a pathological condition, such as reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation induced by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) or the psychosine induced arachidonic acid (AA) accumulation, endogenous alpha-synuclein (αSyn), and fatty acid-binding protein 7 (FABP7) interact with each other and form FABP7-positive oligomers. This process may result in oligodendrocyte loss. In addition, ligand 6 disrupted the FABP7–αSyn interaction and inhibited αSyn oligomerization, thereby improving OLGs survival.