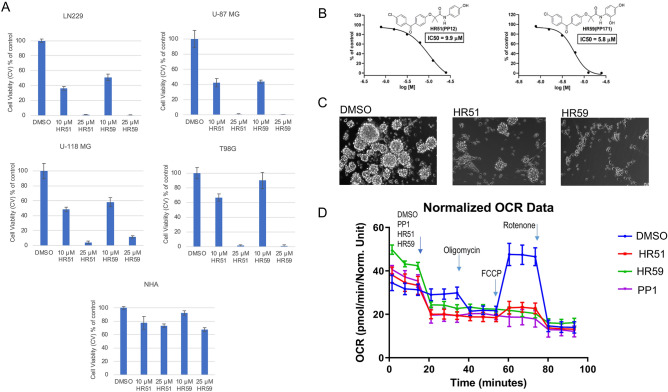
Figure 9.
Cytotoxic effects of selected HR compounds. (A) Effects of 10 and 25 μM of HR51 and HR59 on the survival of human glioblastoma cell lines, LN229, U-87MG, U-118 MG, and T98G, compared to the effects of these two compounds on the survival of normal human astrocytes (NHA; LONZA/Clonetics™). Data were collected after 72 h of a continuous cell exposure to a single dose of HR51 or HR59 in the low glucose medium (1 g/L). Cells treated with DMSO (vehicle) were used as control. Data are expressed as cell viability (MTT, % of control) and represent average values with standard deviation (n = 3). (B) Dose response curves and IC50 values calculated for two most promising HR compounds, HR51 and HR59. Cell viability was evaluated by the MTT assay performed after exposure of LN229 to HR51 and HR59 for 72 h. Data represent mean values ± SD (n = 3). (C) Effects of HR51 and HR59 (25 μM each) on the sphere formation by patient-derived glioblastoma isolates (GBM12). In the sphere formation assay, low density single cell suspension of GBM12 cells was exposed to the serum-free stem-cell supporting medium (StemPro NSC SFM; Gibco: A1050901) supplemented with Recombinant Human FGF Basic and EGF (10 μg each), as previously reported66,72. The cells were allowed to form spheres for 5 days in the presence or absence of HR51 and HR59. DMSO-treated cultures (vehicle) were used as positive control for the sphere formation. In this condition, GBM12 cells grow in suspension and display stem-like phenotype—formation of multicellular gliospheres in low density cultures66. (D) Metabolic effects of HR51 and HR59 compared to the prototype drug, PP1. Metabolic responses to the drugs were evaluated in LN229 using Extracellular Flux Analyzer XF96 (Seahorse/Agilent). The oxygen consumption rate (OCR; indicative of mitochondrial respiration) was evaluated after injecting DMSO, (negative control), PP1 (positive control) and two experimental drugs, HR51 and HR59, followed by sequential injections of oilgomycin, FCCP, and rotenone (mitochondrial stress assay). Average OCR data were calculated from three independent experiments. Data represent average values ± SD. Compared to negative control (DMSO), all tested metabolic compounds (PP1, HR51 and HR59) triggered an immediate drop in OCR. In addition, the cells treated with these three compounds did not respond to FCCP injection, indicating loss of the proton gradient across the mitochondrial membrane.