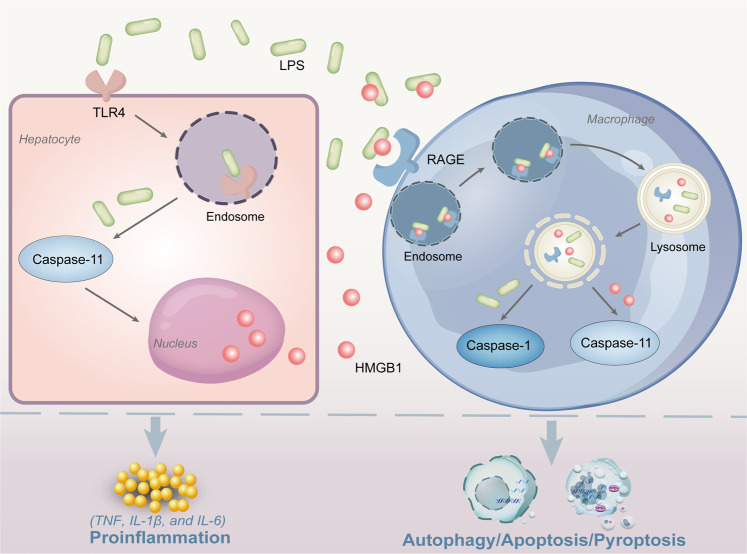
Fig. 1. Release of HMGB1 and its intracellular and extracellular function in LPS-mediated infection and sepsis.
LPS uptake into hepatocytes via TLR4 can activate the caspase-11-mediated pathway to stimulate HMGB1 mobilization from the nucleus and release from hepatocytes. Extracellular HMGB1 can deliver LPS to macrophages. Subsequently, endosomal and lysosomal rupture in macrophages leads to the release of HMGB1 and LPS into the cell cytosol and activates caspase-11 and caspase-1 signaling. Consequently, HMGB1 induces a systemic inflammatory response through TNF, IL-1, and IL-6 and triggers cell apoptosis, autophagy, and pyroptosis. LPS lipopolysaccharide, HMGB1 high mobility group box 1, TLR4 Toll-like receptors.