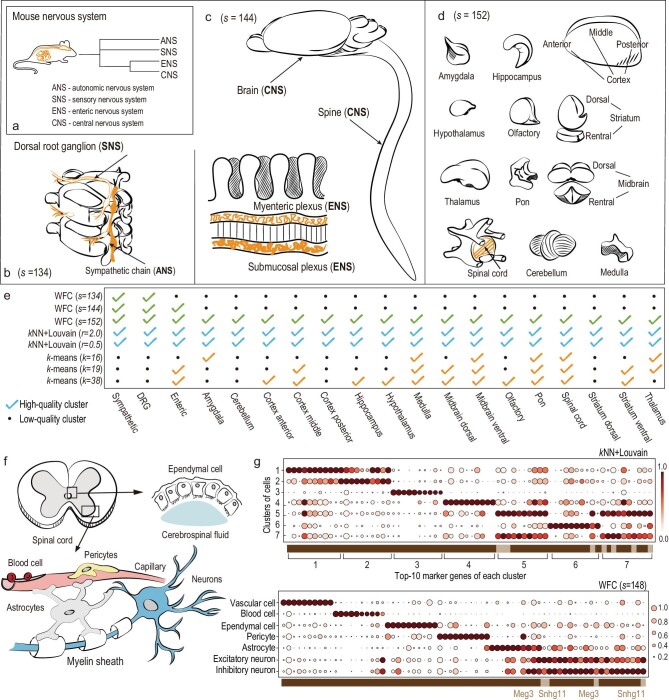
Figure 3.
Clustering 507 286 single cells of the mouse nervous system and 37 221 spinal cord cells. (a) Illustration of anatomical regions of the mouse nervous system, and a high-level clustering hierarchy established by WFC. (b–d) Nervous tissues (clusters) identified by WFC over three different scales. (e) Results of clustering all nervous single cells. High-quality clusters are with at least 100 cells and 0.9 purity score [24]. (f) Illustration of the main cell types of the spinal cord. (g) Clustering spinal cord cells using WFC and kNN + Louvain. Top-10 marker genes of each cluster (at least 100 cells) are plotted as circles. Color darkness represents the mean expression of this gene (min-max normalized), and circle size represents the fraction of cells expressing this gene within the corresponding cluster. A marker gene may belong to a single cluster or multiple clusters, represented by dark and light brown grids respectively in the horizontal axis. WFC detects seven clusters identifying specific cell types. kNN + Louvain finds 30 clusters (Supplementary Fig. 6), and the best seven are plotted here.