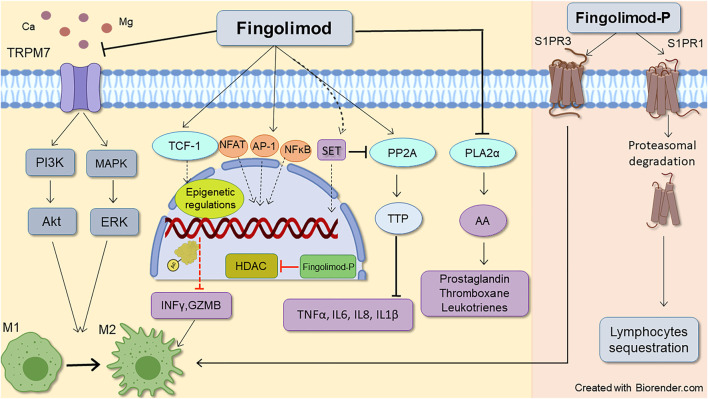
FIGURE 2.
Schematic representative of fingolimod anti-inflammatory mode of action. Fingolimod main immunomodulatory action occurs through downregulating S1P receptors1, leading to lymphocytes sequestration. Its action on S1P receptors3 also favors lymphocytes M2 anti-inflammatory phenotype which is mediated by STAT3 phosphorylation. Besides, non-S1P related actions of fingolimod also can reduce inflammatory response by decreasing inflammatory molecules, T-cell inhibition, and shifting microglia and macrophages toward M2 phenotype. Enhancing histone acetylation by epigenetic regulation, phospholipase A2α inhibition, and activation of PL2A (through inhibition of SET expression) by fingolimod reduces inflammatory cytokines such as TNFα, IL6, IL8, and IL-1β. The drug also inhibits PLA2α (which contributes to AA release and subsequent prostaglandins production), and TRPM7 chanzyme (which can induce both pro and anti-inflammatory phenotypes in macrophages). AA, Acid arachidonic; AP-1, Activator protein 1; Fingolimod-P, Fingolimod phosphate; GZMB, granzyme B; HDACi, Histone deacetylate inhibition, IL (6, 8), Interleukin (6, 8); INFϒ, interferon-gamma; M1, Pro-inflammatory macrophage/microglia; M2, Anti-inflammatory macrophage/microglia NFAT1, Nuclear factor of activated T-cells 1; NFκB, Nuclear factor-kappa B; PLA2α, Phospholipase 2α; PP2A, Protein phosphatase 2A; TCF-1, T cell factor 1; TNFα, Tumor necrosis factor alpha; TTP, Tristetraprolin.