FIGURE 3.
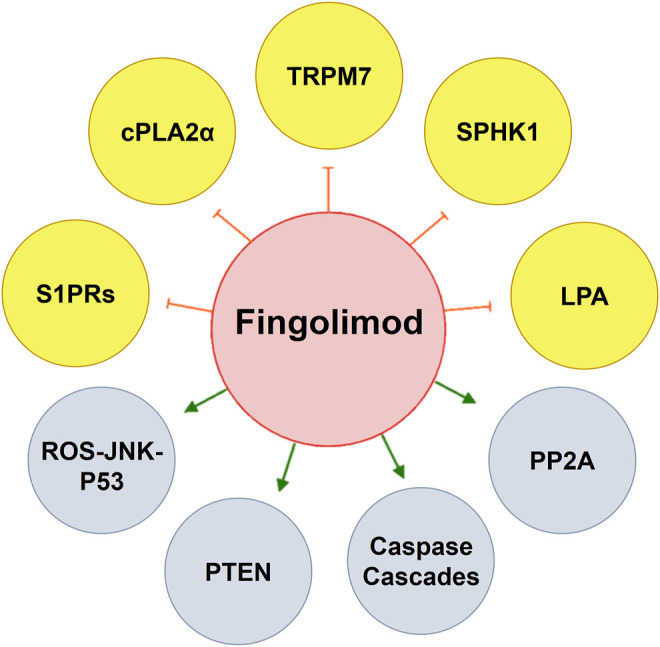
By modulating key pathways in oncogenesis, fingolimod has the potential use for cancer therapy. Fingolimod activates PP2A that plays a principal role as a regulator of cell cycle/division and growth. Fingolimod can induce apoptotic pathways by activation of caspase cascades, enhancing PTEN which inhibits pAkt, and inducing (ROS-JNK-p53) loop-dependent autophagy. By modulating S1PRs, fingolimod anti-angiogenesis activity is also a help in cancer treatment. Antiproliferative effects on fingolimod at some points occur by inhibiting TRPM7, cPLA2α, SPHK1, and LPA which makes the drug an interesting object in cancer research. cPLA2α, cytosolic phospholipase A2; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; PP2A, protein phosphatase 2A; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; S1PR, sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor; SPHK, sphingosine kinase; TRPM7, transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M; ROS-JNK-P53, reactive oxygen species-c-Jun N-terminal kinase-protein 53.
