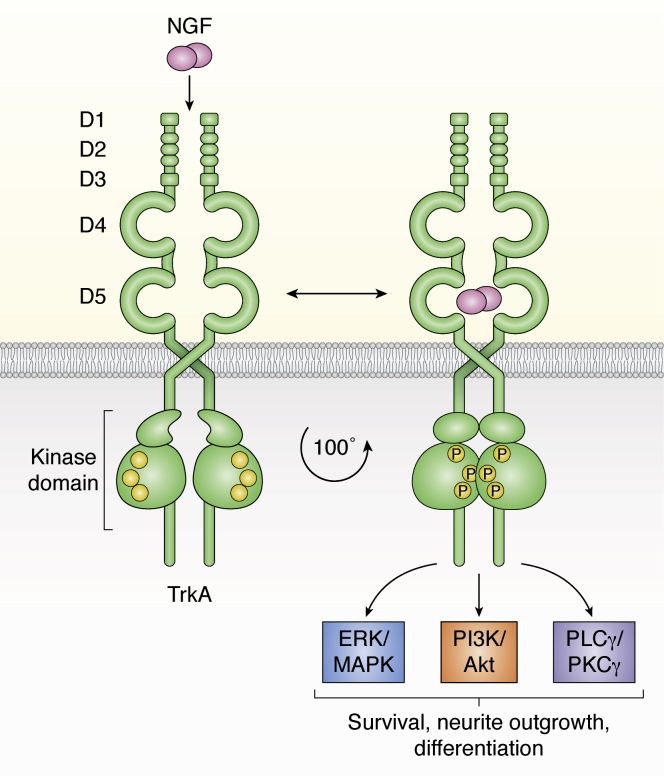
Figure 1.
TrkA receptor structure and signaling pathways. The TrkA receptor consists of five extracellular domains (D1–D5), an α-helical transmembrane domain, and an intracellular segment containing a kinase domain. The receptor can exist in preformed inactive dimers. NGF binding to TrkA activates the receptor, causing rotation and rearrangement of the dimers to an active state, autotransphosphorylation, and activation of multiple signaling pathways. TrkA receptor is shown in green, NGF dimers in pink, and phosphorylated sites of the active kinase domain as a “P”. PLC-γ, phosphoinositide phospholipase C-γ; PKC-γ, protein kinase C-γ; Trk, tropomyosin receptor kinase.