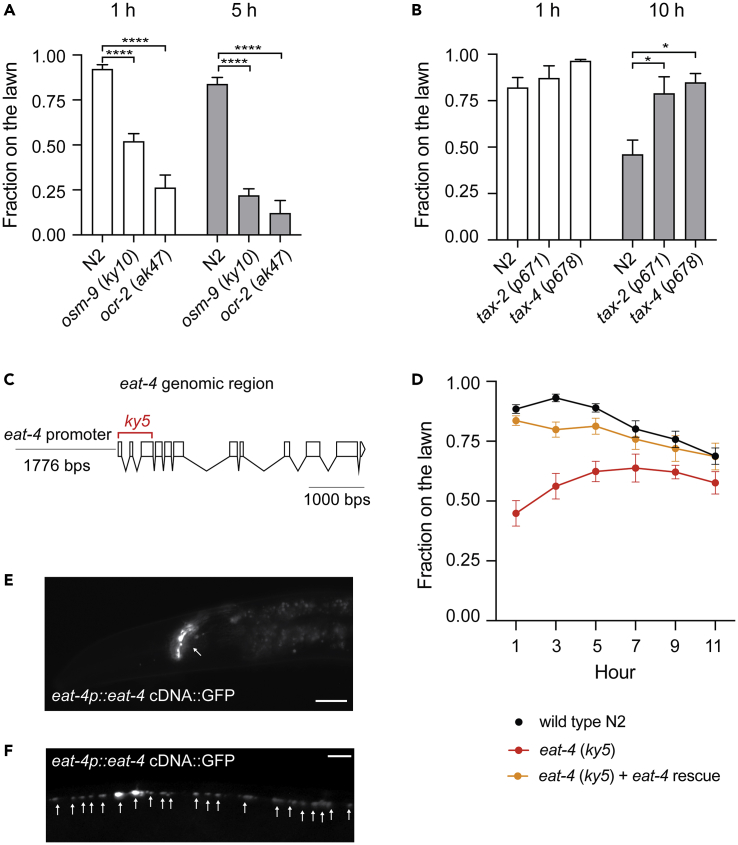
Figure 1.
Glutamate transmission mediates C. elegans behavioral response to P. aeruginosa PA14
(A–B) Sensory signal transduction plays antagonistic roles in regulating C. elegans behavioral response to P. aeruginosa PA14. (A) osm-9 (ky10) and ocr-2 (ak47) mutants elicit heightened avoidance responses to a lawn of P. aeruginosa PA14, (B) tax-2 (p671) and tax-4(p678) mutants elicit delayed avoidance responses to a lawn of P. aeruginosa PA14. (A–B) Error bar represents SEM ∗ represents p < 0.05. ∗∗∗∗ represents p < 0.0001. As determined by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison analysis. N = 10.
(C) Scheme of the eat-4 genomic region. The deleted region in eat-4(ky5) mutant is indicated in red.
(D) Time course experiments of pathogen avoidance response of wild type N2, eat-4(ky5) and eat-4(ky5) + eat-4 rescue. At 5h, N2 verses eat-4(ky5) is p < 0.0001. At 7h, N2 verses eat-4(ky5) is p < 0.001. Both at 5 and 7h, N2 verses eat-4(ky5) + eat-4 rescue is not significant, as determined by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison analysis. N = 12.
(E–F) Fluorescence micrographs of eat-4p:eat-4:GFP in eat-4 (ky5) background. Punctate GFP signals are present in the nerve ring (E) and along the ventral nerve cord (F). Scale bar indicates 10 μm in (E) and 20 μm in (F)