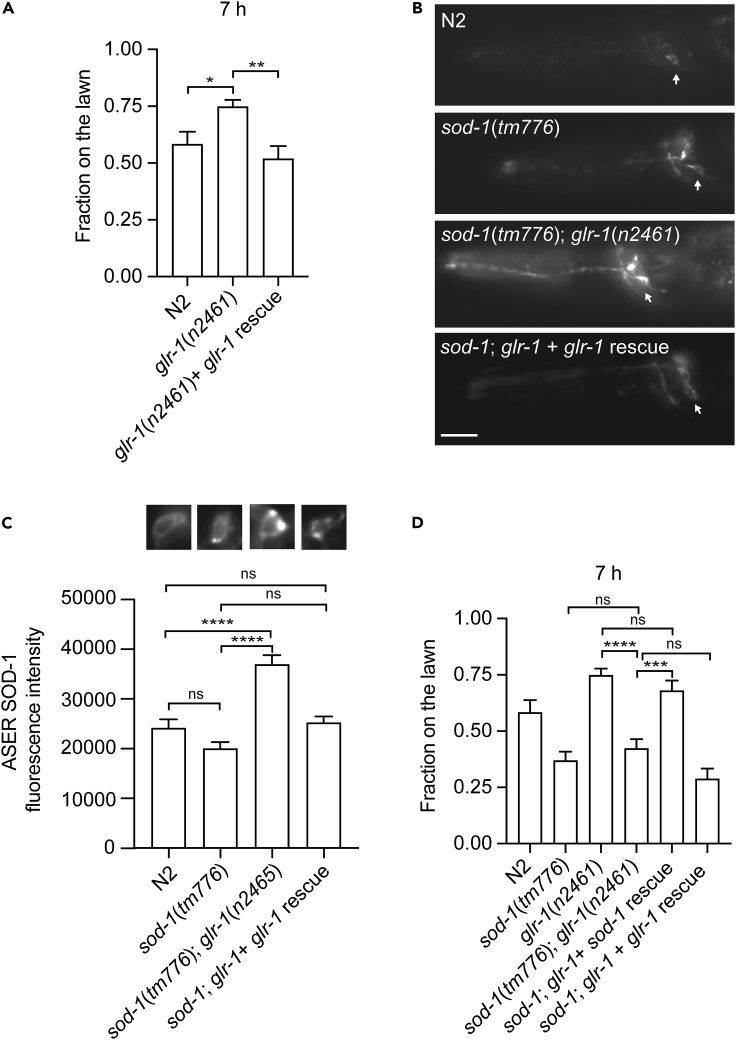
Figure 2.
AMPA-type glutamate receptor promotes C. elegans avoidance response to P. aeruginosa PA14
(A) glr-1(n2461) mutant animals elicit delayed avoidance responses to a lawn of P. aeruginosa PA14. The delayed behavioral response of glr-1(n2461) can be rescued by a construct that contains glr-1p:glr-1:GFP. Error bar represents SEM ∗ represents p < 0.05. ∗∗ represents p < 0.01 As determined by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison analysis. N = 12.
(B) Fluorescence micrographs of sod-1p:sod-1:mRFP transgenic animals in wild type N2, sod-1(tm776), sod-1(tm776); glr-1(n2461), and sod-1(tm776); glr-1(n2461) + glr-1 rescue backgrounds. Arrow indicates ASER neuron. Anterior is to the left. Dorsal is at the top. Scale bar indicates 10 μm.
(C) SOD-1 expression is elevated in the ASER neuron in glr-1(n2461) background. Error bar represents SEM ∗∗∗∗ represents p < 0.0001. ns represents not significant. As determined by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's multiple comparison analysis. N = 34.
(D) sod-1(tm776); glr-1(n2461) mutant animals show a similar pathogen avoidance response to sod-1(tm776) single mutant. The avoidance response of sod-1(tm776); glr-1(n2461) double mutant can be rescued by the sod-1p::sod-1::GFP but not by the glr-1p:glr-1:GFP. Error bar represents SEM ∗∗∗ represents p < 0.001. ∗∗∗∗ represents p < 0.0001. ns represents not significant. As determined by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's multiple comparison analysis. N = 9.