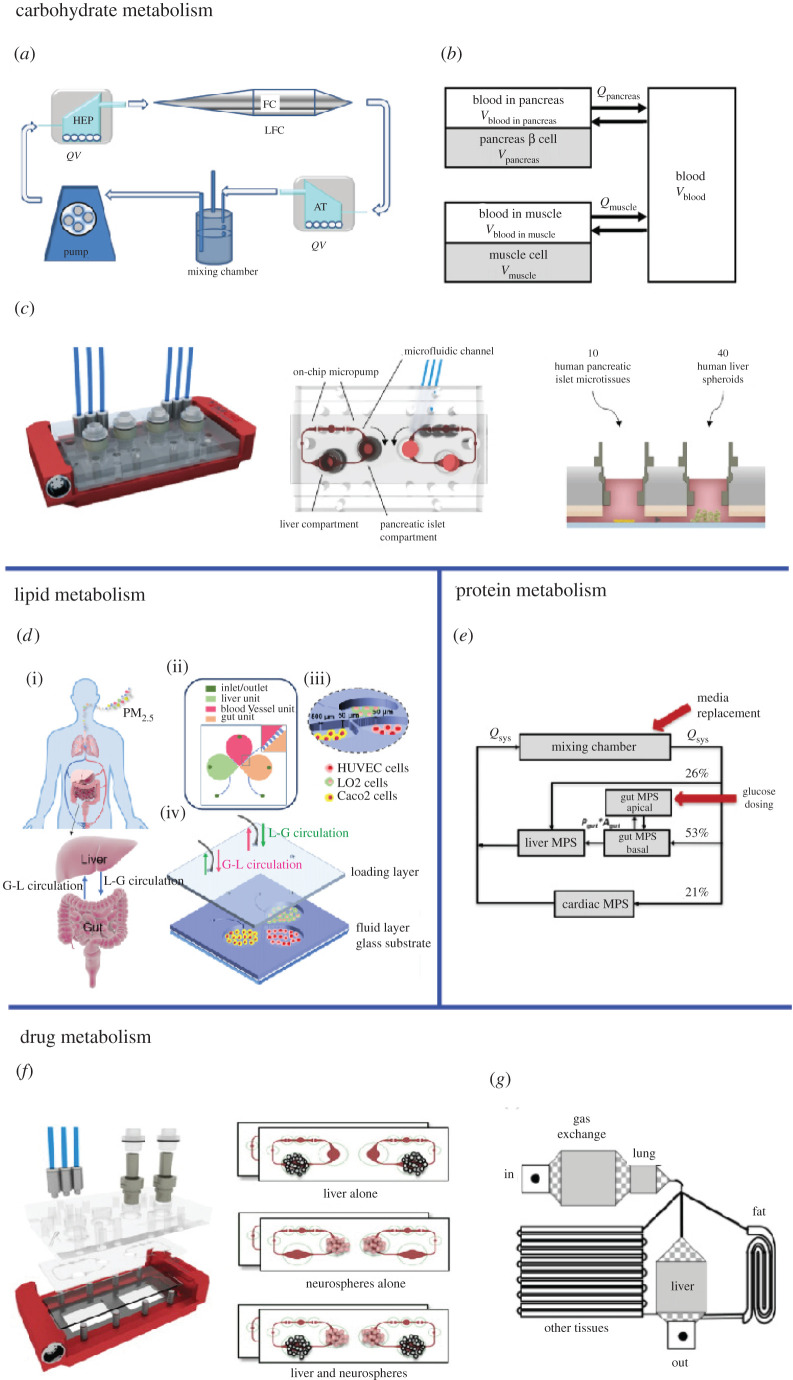
Figure 2.
MOCs to study the various types of metabolism. Carbohydrate metabolism—(a) a three-way connected organ system featuring adipose, liver and vascular tissue (adapted from [68] (CC BY 4.0)), (b) a connected pancreas–muscle tissue model to study insulin-dependent glucose uptake (adapted from [69] © 2019 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.) and (c) a model connecting pancreatic islets and liver spheroids to study insulin signalling between the cell types (reproduced from [70] (CC BY 4.0)). Lipid metabolism—(d) the study of cholesterol dysregulation using a gut–liver-on-chip model (adapted with permission from [71]. Copyright 2021 American Chemical Society). Protein metabolism—(e) connected gut–liver–cardiac system for the study of protein metabolism (adapted from [72] (CC BY 4.0)). Drug metabolism—(f) a neurotoxicity study involving the interaction between liver and neurospheres (reprinted from [73] © 2015 with permission from Elsevier) and (g) accumulation, distribution and toxicity in a liver–fat–lung-on-chip system (adapted from [74] (CC BY 4.0)).