Figure 3.
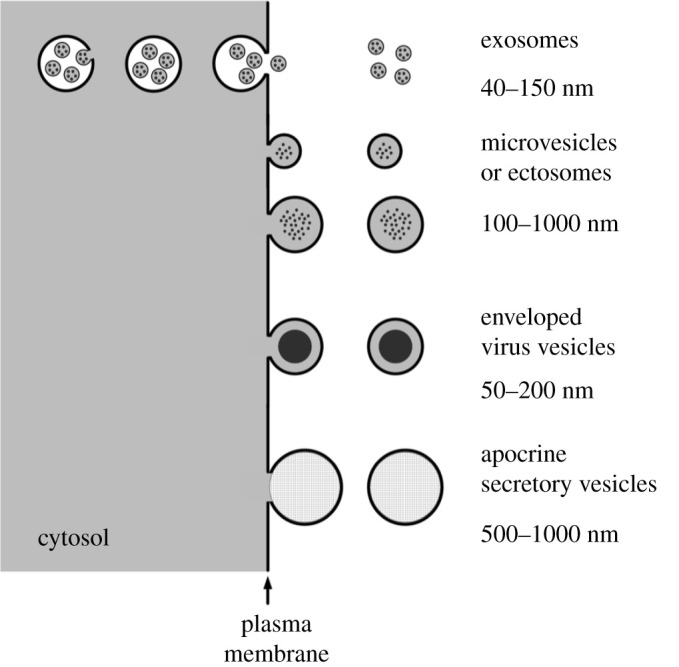
Some of the different kinds of membrane-bound extracellular vesicles secreted from mammalian cells. Exosomes are first budded off into intracellular vacuoles, called multivesicular bodies, before being released into the extracellular fluid when the multivesicular bodies fuse with the plasma membrane. Microvesicles of various types, also called ectosomes, are budded off the plasma membrane directly into the extracellular fluid [89,90]. Vesicles containing viruses, such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), are released within an envelope derived from the cell membrane [91]. Some glandular cells secrete vesicles, like the membrane-bound lipid globules produced by mammary glands as constituents of milk [92]. In addition, when dying cells break up they release membrane-bound ‘apoptotic bodies’ of varying sizes [90].
