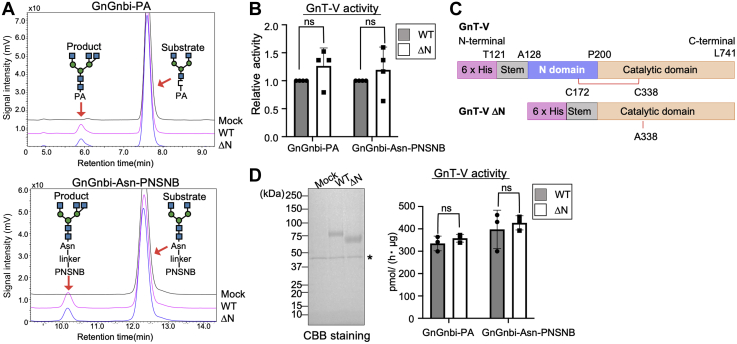
Figure 2.
Enzyme activity of GnT-V WT and ΔN toward oligosaccharide substrates.A, lysates of HeLa cells expressing GnT-V WT or ΔN were reacted with GnGnbi-PA or GnGnbi-Asn-PNSNB as the oligosaccharide acceptor. The acceptor substrates and the GnT-V products were separated using reverse-phase HPLC. B, the activity of GnT-V WT or ΔN calculated by the peak area in (A) (n = 4, means ± S.D.). The samples were collected from independent sets of transfected cells. The p value was calculated by Holm-Sidak’s test. N.S., not significant. C, plasmid constructs of soluble GnT-V WT and ΔN used in this study. D, left, soluble GnT-V WT or ΔN was expressed in COS7 cells and purified from the culture supernatants using Ni2+-beads. Purified GnT-V WT or ΔN was separated by SDS-PAGE and stained with CBB. ∗non-specific band. Right, the activity of purified soluble GnT-V WT or ΔN was measured, same as (A) (n = 3, mean ± S.D.). Three independent assays were carried out using the same purified enzymes. The p value was calculated by 2-way ANOVA and multiple t test. N.S., not significant. GnT-V, N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-V; PA, 2-aminopyridine; PNSNB, (N-(2-(2-pyridylamino)ethyl)succinamic acid 5-norbornene-2,3-dicarboxyimide ester).