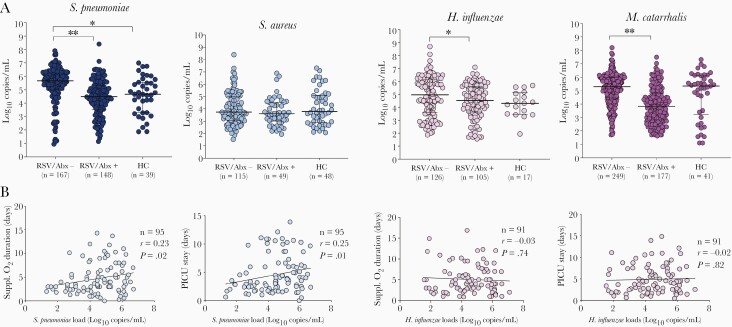
Figure 4.
Bacterial loads in children with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection and healthy controls. A, Bacterial loads in healthy controls and children with RSV infection according to antibiotic use at study enrollment. The horizontal axis represents RSV-infected children not treated with antibiotics (RSV/Abx−), those treated (RSV/Abx+), and healthy controls (HC). The Y-axis represent bacterial loads in log10 copies/mL for each bacterium. Comparisons by Mann-Whitney U test between RSV/Abx− and RSV/Abx+, and between RSV/Abx− and HC. ∗P<.05; ∗∗P<.01. B, Spearman correlations between Streptococcus pneumoniae (blue) and Haemophilus influenzae (pink) loads and duration of supplemental oxygen and pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) stay among patients admitted to the PICU. The number of patients (n), correlation coefficient (r), and P value are included in each plot.