Figure 3.
Thyroid hormone activation induces glutamine addiction
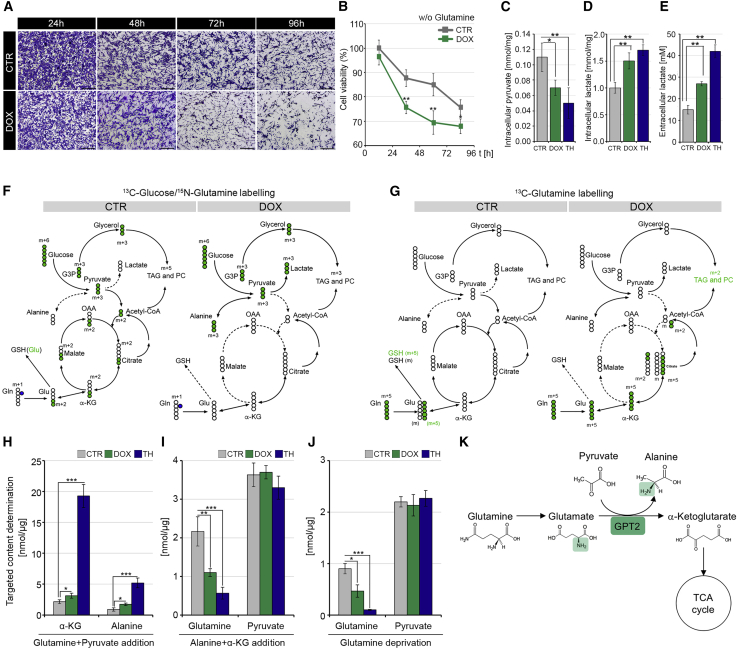
(A) Representative images of C2C12 pTRE-D2 cells cultured in the presence (DOX) or absence (CTR) of 2 μg/mL DOX in DMEM without glutamine at different time points (24, 48, 72, and 96 h). Scale bar, 50 μm.
(B) Cell viability percentage of the same cells as in (A) was determined by MTT assay.
(C–E) Intracellular pyruvate (C), intracellular lactate (D), and extracellular lactate (E) concentrations were measured in C2C12 pTRE-D2 cells cultured for 48 h in the presence of DOX, THs, and in untreated CTR cells by GC-MS analysis. The results are shown as means ± SD from at least 3 separate experiments.
(F and G) Schematic of isotopologue distributions of metabolites derived from either 13C-labeled glucose, 15N-labeled glutamine, (F) or 13C-labeled glutamine (G) in C2C12 pTRE-D2 cells cultured for 48 h in the presence (+DOX) or absence (–DOX) of doxycycline by stable-isotope-resolved metabolomic analysis. Empty circles represent unlabeled atoms; green circles represent labeled carbon (13C), and blue circles represent labeled nitrogen (15N). The arrows indicate the flux of reactions in each of the metabolic pathways. The mass increase (m+1, m+2, m+3, m+5, and m+6) indicates the transfer of labeled atoms among metabolites. G3P, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; TAG, triacylglycerol; PC, phosphatidylcholine; α-KG, alpha-ketoglutarate; Glu, glutamate; Gln, glutamine; GSH, glutathione; OAA, oxaloacetate.
(H–J) Intracellular levels of α-KG, alanine, pyruvate, and glutamine extracted from DOX- or TH-treated C2C12 pTRE-D2 compared with untreated CTR cells and cultivated in a medium containing an excess of either pyruvate and glutamine (H), α-KG and alanine (I), or in the absence of glutamine. Data represent the mean ± SD of the mean of fifteen replicates. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(K) Schematic of GPT2-mediated coupling of glutamine-driven TCA anaplerosis.